- Luật
- Hỏi đáp
- Văn bản pháp luật
- Luật Giao Thông Đường Bộ
- Luật Hôn Nhân gia đình
- Luật Hành Chính,khiếu nại tố cáo
- Luật xây dựng
- Luật đất đai,bất động sản
- Luật lao động
- Luật kinh doanh đầu tư
- Luật thương mại
- Luật thuế
- Luật thi hành án
- Luật tố tụng dân sự
- Luật dân sự
- Luật thừa kế
- Luật hình sự
- Văn bản toà án Nghị quyết,án lệ
- Luật chứng khoán
- Video
- NGHIÊN CỨU PHÁP LUẬT
- ĐẦU TƯ CHỨNG KHOÁN
- BIẾN ĐỔI KHÍ HẬU
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự
- Dịch vụ pháp lý
- Tin tức và sự kiện
- Thư giãn

TIN TỨC
fanpage
Thống kê truy cập
- Online: 223
- Hôm nay: 198
- Tháng: 1621
- Tổng truy cập: 5245625
2020 highlights
Goodbye 2020, and hello 2021!
These were our top 20 most viewed blogs of 2020, in reverse order.
Amid all the doom and gloom in the world, some impressive scientific discoveries and technological breakthroughs occurred, as we hope you'll agree!
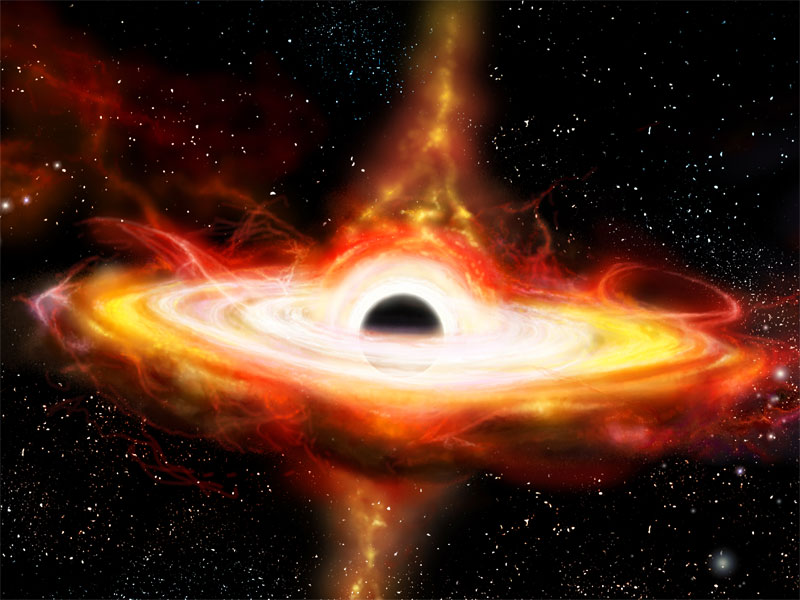
Fastest-growing black hole identified
In July 2020, astronomers at the Australian National University (ANU) reported that J2157 is now known to have 34 billion solar masses and is consuming the equivalent of our Sun's mass every day, making it the fastest-growing black hole ever detected in the Universe.

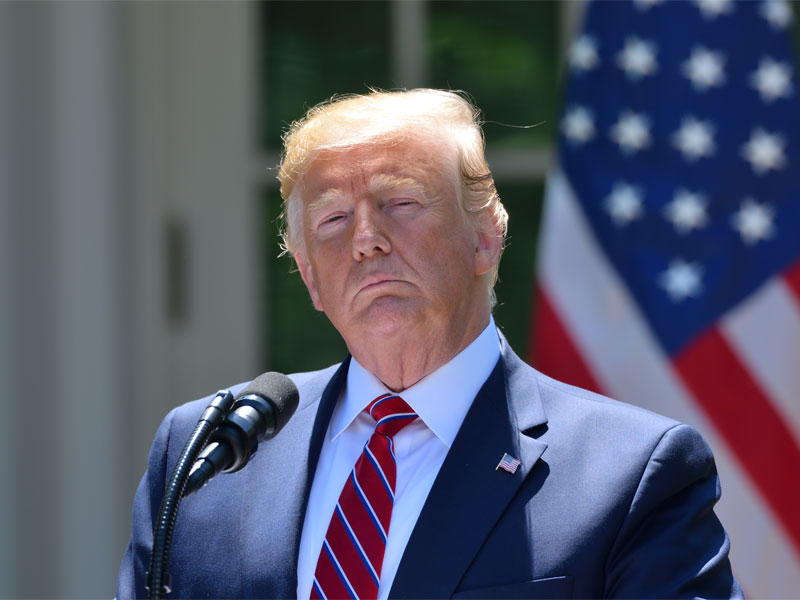
Election model predicts landslide defeat for Trump
In May 2020, a model by Oxford Economics predicted that Trump would lose the electoral college by 328 to 210.

World's fastest Internet speed: 44.2 Tbps
In May 2020, Australian scientists achieved a new world's fastest Internet speed using a single optical chip, at 44.2 terabits per second (Tbps), which is about a million times faster than a typical home broadband connection.
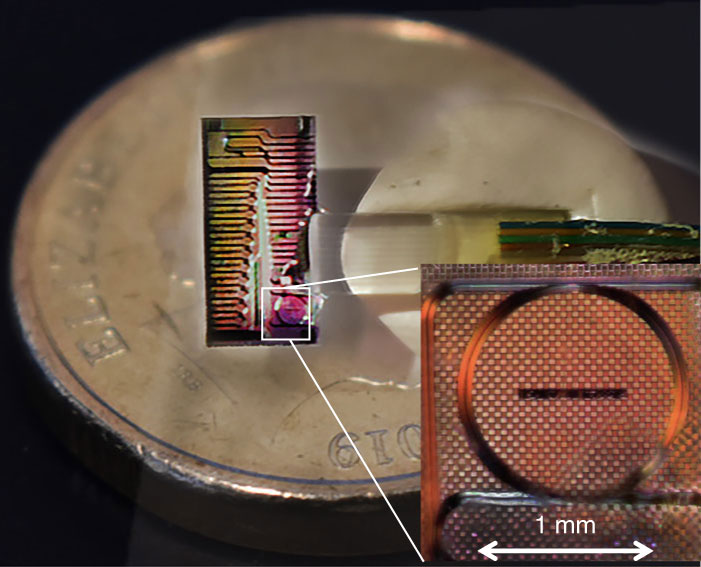
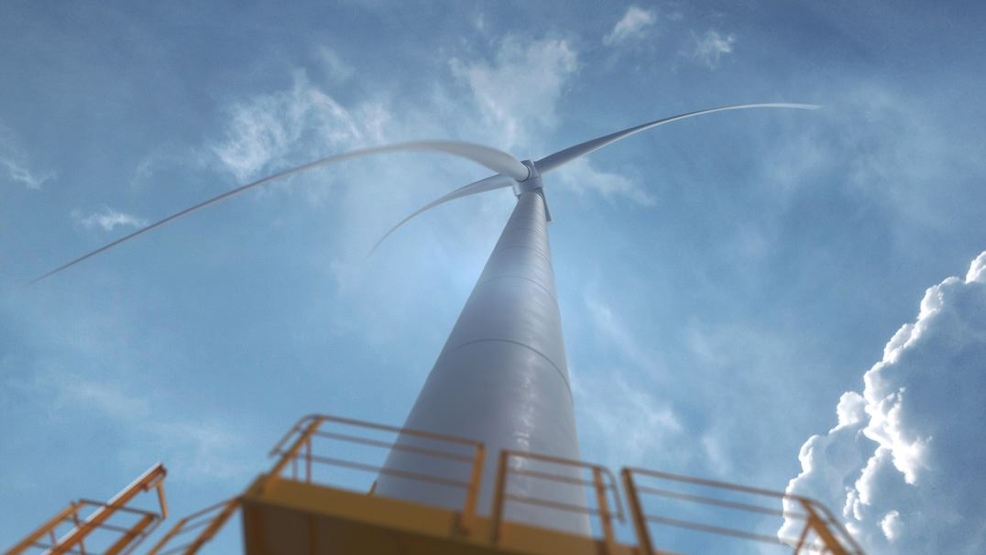
Giant new offshore wind turbine to debut in 2024
In May 2020, Spanish engineering company Siemens Gamesa revealed the SG 14-222 DD – a new offshore wind turbine, set to become the world's largest and most powerful, with serial production planned for 2024.

First passengers travel safely on a Hyperloop
In November, the team at Virgin tested human travel in a Hyperloop pod for the first time.
CRISPR-based treatment destroys two cancer types
In November, researchers at Tel Aviv University (TAU) in Israel demonstrated that the CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing system is highly effective in treating brain and ovarian cancers, without side effects.
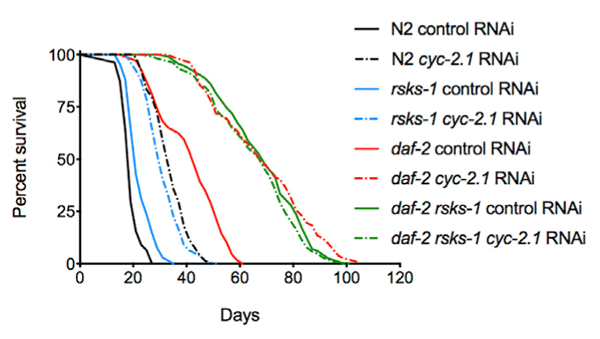
Longevity breakthrough: 500% increase in nematode lifespan
Progress with longevity extension continued in 2020. Among the more impressive breakthroughs in animal models occurred in January, when scientists identified "synergistic cellular pathways" to amplify the lifespan of C. elegans by as much as 500%.
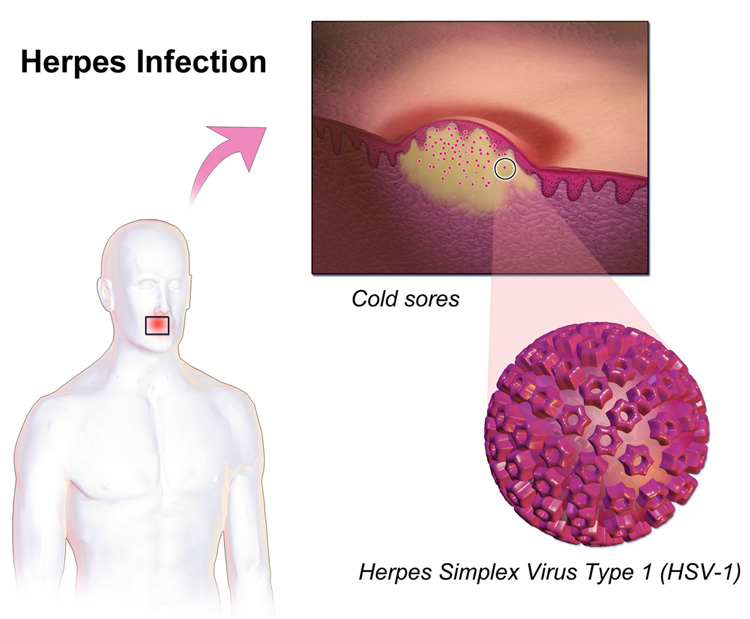
Progress towards a cure for herpes
In August, scientists used gene editing to remove latent herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1), also known as oral herpes, from mice.
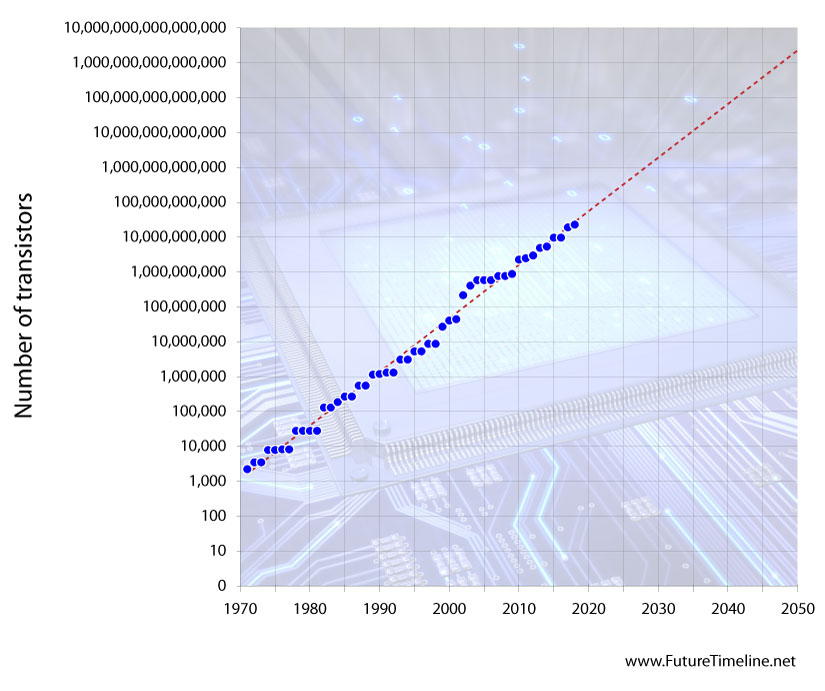
50-fold increase in transistor density is possible by 2030
In August, Intel's Chief Architect, Raja Koduri, presented a roadmap for increasing the number of transistors able to fit on a chip by a factor of 50. This could enable the trend of exponential progress in computer technology, known as Moore's Law, to continue.
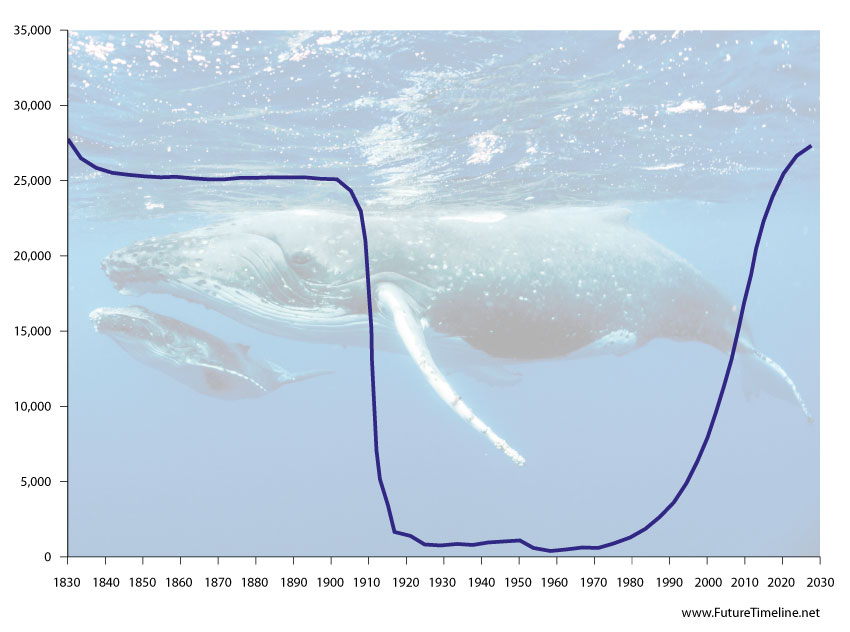
World's oceans can be restored by 2050
We often hear gloomy predictions about the environment. However, returning marine life to abundance "is at least technically feasible" by 2050, according to an international study published in April 2020, which cites humpback whale numbers as an example of what can be achieved.
COVID-19 is natural, not man-made
In March 2020, scientists published a peer-reviewed study in the journal Nature Medicine, finding no evidence that COVID-19 was made in a laboratory or otherwise engineered – based on detailed analysis of public genome data from SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses.
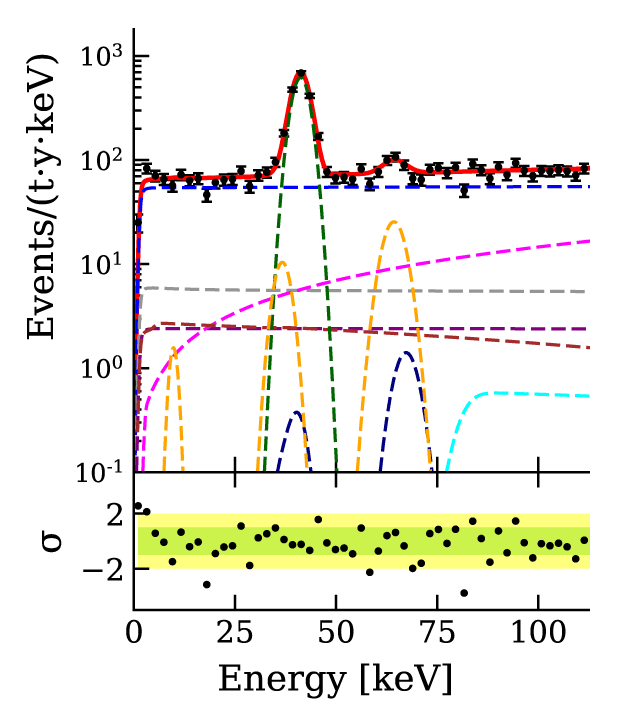
Possible first detection of axion particle
In June 2020, physicists at the XENON dark matter research facility in Italy reported an "excess" of 53 events, which may hint at the existence of hypothetical particles called solar axions.
Largest known black hole merger is confirmed
A major astronomical discovery occurred in September 2020, when researchers confirmed the largest known black hole merger. This also provided the first clear evidence of an intermediate-mass black hole – lying mid-way between a regular black hole and the supermassive giants at the centre of galaxies.
Superconductivity achieved at 15°C
After more than a century of research in this field, a room-temperature superconductor finally emerged in 2020, when a team from two universities in the USA demonstrated a material able to work at 15°C – an improvement of 28°C over the previous record. In the future, this technology could have revolutionary potential in all kinds of areas, such as new hovering or flying vehicles, quantum computers, and major advances in energy.

A potentially major breakthrough in anti-aging medicine
Another of the predictions on our timeline became a reality in 2020, when scientists presented evidence that young blood plasma given to older mice reduced aging by an average of 54% across multiple tissues; and had an impact on various other signs of aging. Longevity expert Aubrey de Grey had predicted major progress in the field back in 2008 (see video below).
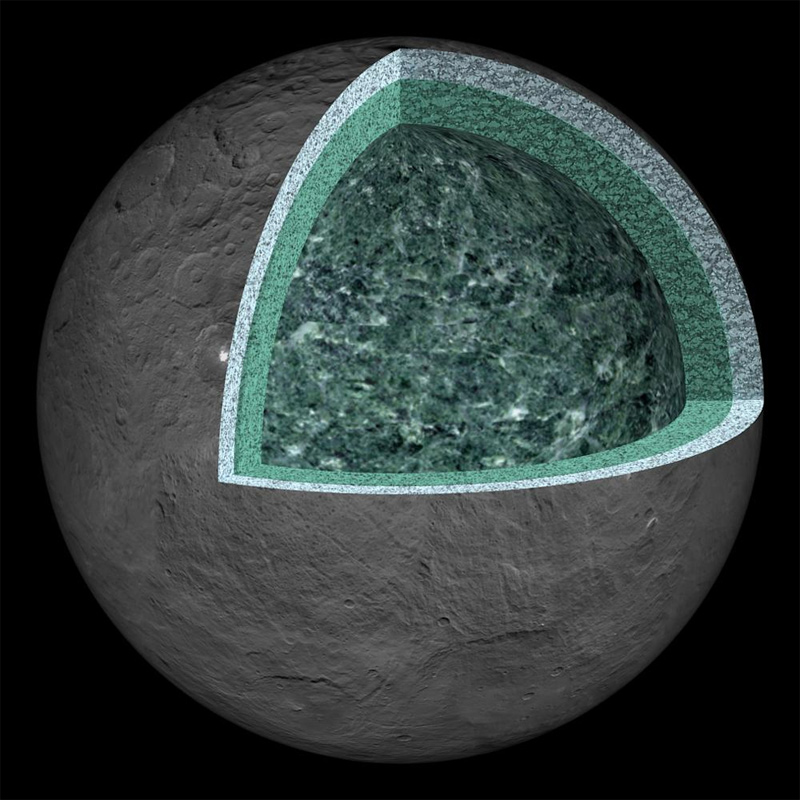
Ceres confirmed to be water-rich world
In August, researchers confirmed that the dwarf planet Ceres is a water-rich body, containing a deep reservoir of brine, based on analysis of gravity data and other measurements from the Dawn probe.
Apophis asteroid may be heading for Earth in 2068
Observations of the near-Earth asteroid, Apophis, have already ruled out a collision with our planet in 2029 and 2036. However, the discovery of a new orbital characteristic in October 2020 suggests that a collision in the year 2068 remains a possibility.
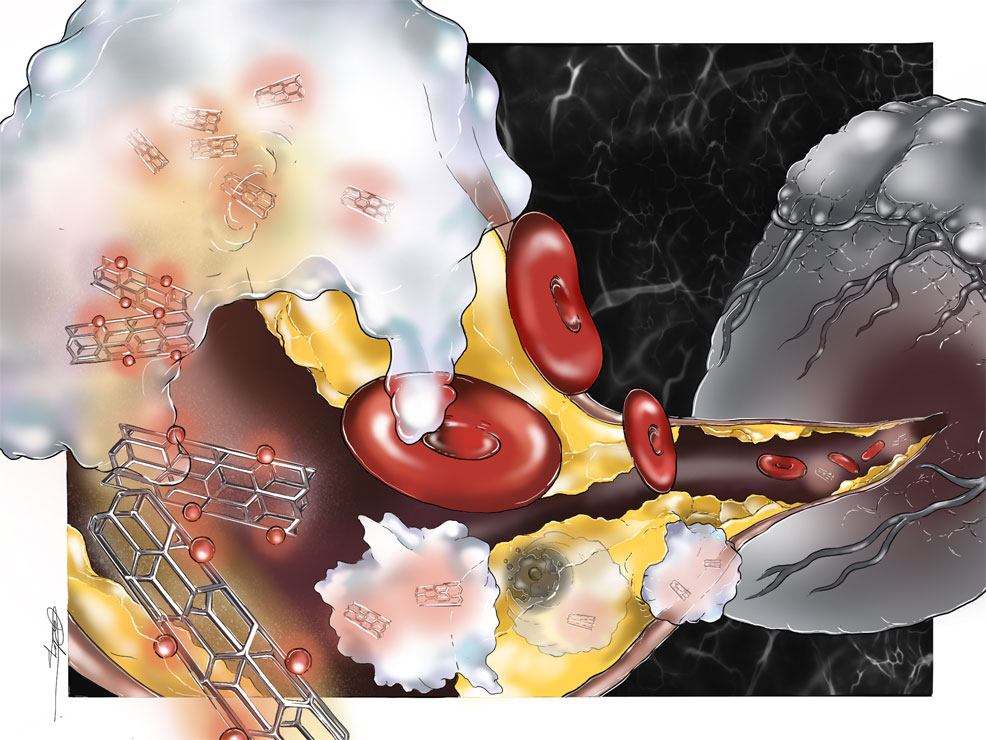
Nanoparticle eats away plaque that causes heart attacks
In February 2020, Michigan State University and Stanford University scientists created a nanoparticle that eats away – from the inside out – portions of plaques that cause heart attacks.
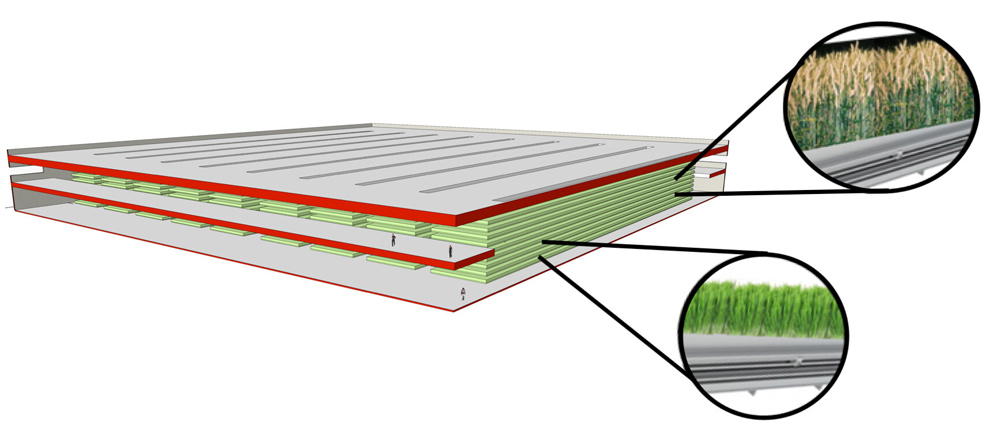
Vertical farming of wheat: up to 600 times greater yield
In August 2020, a study found that wheat grown using a 10-layer, indoor vertical farm could – in theory – have a yield between 220 and 600 times greater than current farming methods.
New algorithm provides 50 times faster deep learning
In November, AI research company Numenta announced a major performance improvement in deep learning networks. Their new system, based on a principle of the brain called "sparsity", enables a 50-fold leap in processing speed – once again demonstrating the rapid rate of progress in forms of information technology.
Các bài viết khác
- Từ sự kiện Tổng biên tập báo TIME Greta Thunberg là Nhân vật của năm 2019 đến báo cáo Biến đổi khí hậu Phúc trình của IPCC báo động đỏ cho nhân loại 82021 (15.01.2020)
- Bộ trưởng Nguyễn Chí Dũng: Giờ là lúc làm trung tâm tài chính quốc tế (11.01.2021)
- ĐẦU NĂM ĐỌC LẠI TÂY DU (11.01.2021)
- 4.000 ngày thay đổi Việt Nam (28.12.2020)
- Tuyến Metro Số 2 Bến Thành - Tham Lương là tuyến metro xuyên tâm dài nhất TP.HCM. (28.12.2020)


















































 Yahoo:
Yahoo: 