- Luật
- Hỏi đáp
- Văn bản pháp luật
- Luật Giao Thông Đường Bộ
- Luật Hôn Nhân gia đình
- Luật Hành Chính,khiếu nại tố cáo
- Luật xây dựng
- Luật đất đai,bất động sản
- Luật lao động
- Luật kinh doanh đầu tư
- Luật thương mại
- Luật thuế
- Luật thi hành án
- Luật tố tụng dân sự
- Luật dân sự
- Luật thừa kế
- Luật hình sự
- Văn bản toà án Nghị quyết,án lệ
- Luật chứng khoán
- Video
- NGHIÊN CỨU PHÁP LUẬT
- ĐẦU TƯ CHỨNG KHOÁN
- BIẾN ĐỔI KHÍ HẬU
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự
- Dịch vụ pháp lý
- Tin tức và sự kiện
- Thư giãn

TIN TỨC
fanpage
Thống kê truy cập
- Online: 223
- Hôm nay: 198
- Tháng: 1621
- Tổng truy cập: 5245625
Food Insecurity: Outlook for 2023
The food gap between advanced and developing economies is growing.
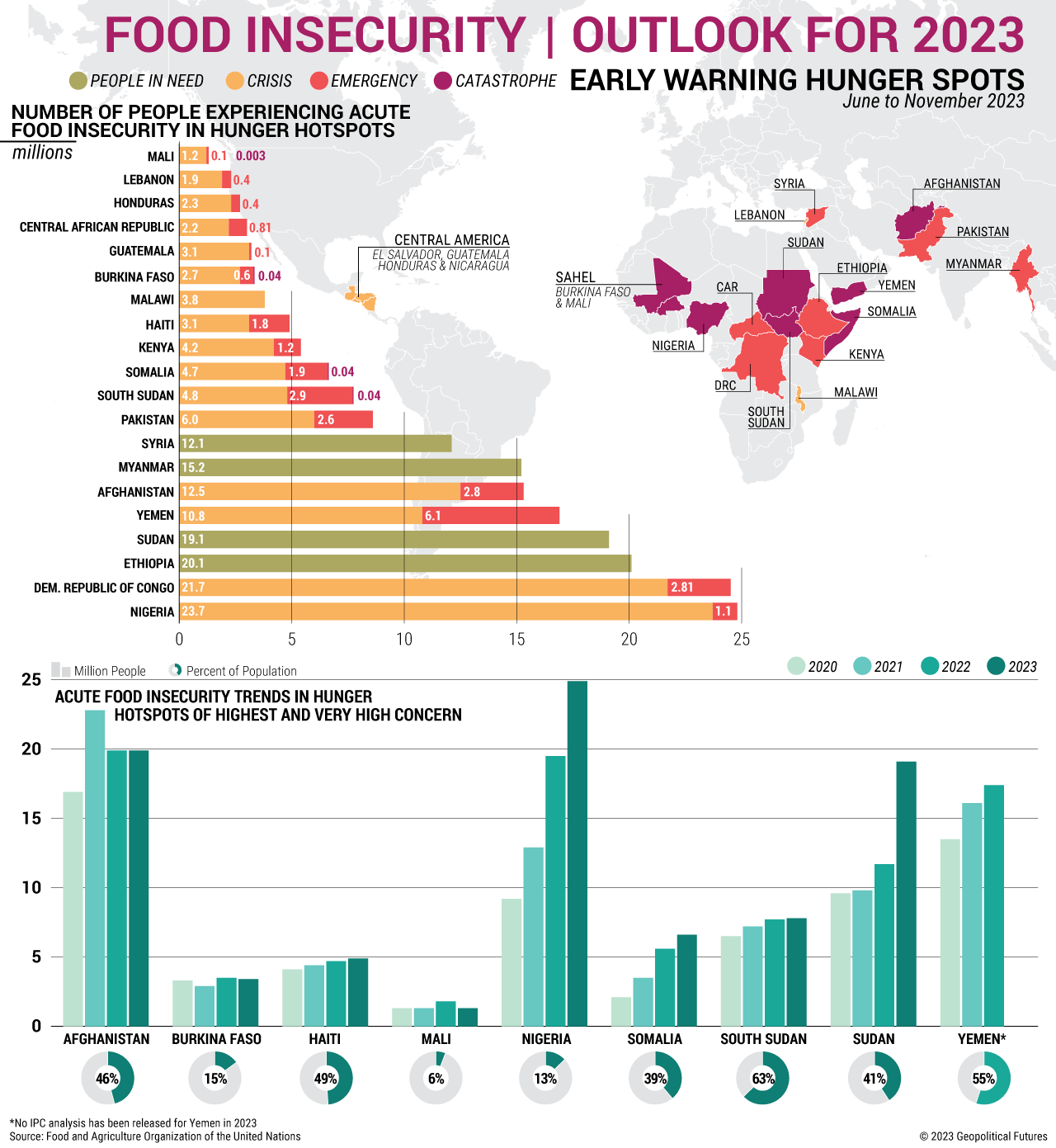
Over the course of 2022, global food prices gradually began to ease. However, this wasn’t necessarily reflected in prices at local markets in countries experiencing food insecurity. Countries that rely on food imports and have low foreign reserves are at greatest risk of seeing a lack of access to food. Costly agricultural input materials, labor and energy also contribute to high food costs.
Notably, the food gap between advanced and developing economies is growing. Developed countries tend to have stronger currencies and better access to credit, meaning food supplies and input materials are generally more affordable and accessible than in developing economies. The most vulnerable countries, however, are often forced to work with institutions like the International Monetary Fund to secure financing to pay for imports. Different countries have varying degrees of success in these negotiations, but it’s generally a challenging path as meeting IMF requirements is for many governments constrained by political considerations at home.
Các bài viết khác
- Vài nét Dự báo thời đại phục hưng và khai sáng của loài người sau đại dịch Corona-2019.7-2021(khởi đầu từ tháng 9 năm giáp thìn 2024) (25.06.2021)
- Từ sự kiện Tổng biên tập báo TIME Greta Thunberg là Nhân vật của năm 2019 đến báo cáo Biến đổi khí hậu Phúc trình của IPCC báo động đỏ cho nhân loại 82021 (15.01.2020)
- Vì sao thiếu điện? (12.06.2023)
- Đột phá công nghệ: Năng lượng nhiệt hạch có kịp cứu thế giới? (12.06.2023)
- Hồi kết của 40 năm tiền rẻ (12.06.2023)


















































 Yahoo:
Yahoo: 