- Luật
- Hỏi đáp
- Văn bản pháp luật
- Luật Giao Thông Đường Bộ
- Luật Hôn Nhân gia đình
- Luật Hành Chính,khiếu nại tố cáo
- Luật xây dựng
- Luật đất đai,bất động sản
- Luật lao động
- Luật kinh doanh đầu tư
- Luật thương mại
- Luật thuế
- Luật thi hành án
- Luật tố tụng dân sự
- Luật dân sự
- Luật thừa kế
- Luật hình sự
- Văn bản toà án Nghị quyết,án lệ
- Luật chứng khoán
- Video
- NGHIÊN CỨU PHÁP LUẬT
- ĐẦU TƯ CHỨNG KHOÁN
- BIẾN ĐỔI KHÍ HẬU
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự
- Dịch vụ pháp lý
- Tin tức và sự kiện
- Thư giãn

TIN TỨC
fanpage
Thống kê truy cập
- Online: 223
- Hôm nay: 198
- Tháng: 1621
- Tổng truy cập: 5245625
A Timeline of North Korea’s Missile Launches and Nuclear Detonations
The North Korean weapons program now testing U.S. President Donald Trump stretches back decades, when the regime began reverse-engineering Scud missiles acquired from Egypt. International efforts to curb North Korea’s nuclear threat were dealt a setback in 2006 with the country’s first successful bomb test, and former leader Kim Jong Il abandoned talks a few years later. His son and successor, Kim Jong Un, has only accelerated the program, testing more sophisticated technology in defiance of international sanctions.
Here’s a detailed history of North Korea’s weapons programs:
1976-81: North Korea begins missile development using Scud-B from the Soviet Union and launchpad from Egypt
1984: First Scud-B missile test firing
1988: Operational deployment of Scud-B and Scud-C missiles
1990: First Rodong missile test firing
July 1994: North Korea’s founding leader Kim Il Sung dies, allowing son and heir Kim Jong Il to assume full leadership
1998: Operational deployment of Rodong missiles, which have a range of 1,300 kilometers (800 miles). Firing of Taepodong-1 missile, which North Korea says was satellite launch
January 2002: U.S. President George W. Bush cites weapons programs in placing North Korea alongside Iran and Iraq in an “axis of evil”
2003: North Korea withdraws from the Non-Proliferation Treaty, begins acquiring weapons-grade plutonium from spent fuel rods. First so-called six-party talks held to resolve concerns over the country’s activities, including China, Japan, Russia, South Korea and the U.S.
2005: North Korea announces possession of nuclear weapons and its withdrawal from six-party talks aimed at ending its atomic program
July 2006: Test firings of Taepodong-2, Rodong and Scud missiles. The Taepodong-2 is a long-range missile that capable of traveling 15,000 kilometers and striking U.S. targets. Even so, analysts say it’s mostly used to launch satellites and would be difficult to convert into a rocket that can deliver weapons
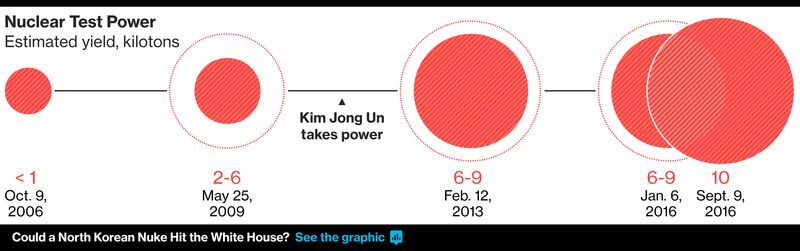
October 2006: The official Korean Central News Agency announces a “successful nuclear test”
2007: Operational deployment of Rodong missiles
April 2009: Firing of Taepodong-2 missile, which North Korea says was satellite launch. United Nations strengthens sanctions and North Korea withdraws from six-party talks
May 2009: North Korea carries out second nuclear test
July 2009: Test-firing of Scud and Rodong missiles

Kim Jong-Il’s funeral procession in Pyongyang on Dec. 28, 2011
December 2011: North Korean leader Kim Jong Il dies, clearing way for Kim Jong Un to take power
April 2012: North Korea reports failed Unha-3 rocket launch
December 2012: North Korea launches Unha-3 rocket that puts its first satellite into space
February 2013: North Korea conducts third underground nuclear test
August 2013: North Korea reported to have restarted nuclear reactor to produce plutonium
May 2015: North Korea claims to have tested a submarine-launched missile; says it developed technology to mount nuclear warhead on a missile
North Korea’s underwater ballistic missile launch in May 2015.
July 2014: North Korea conducts series of missile tests ahead of Chinese President Xi Jinping’s visit to Seoul
September 2015: North Korea threatens nuclear attack against U.S. and reaffirms its main reactor is operational. South Korean President Park Geun-hye says North will “pay a price” for fourth test
December 2015: Kim Jong Un says North Korea is “ready to detonate” a hydrogen bomb
Jan. 6, 2016: North Korea says it successfully tests hydrogen bomb
Feb. 7, 2016: North Korea launches a long-range rocket that it says successfully put a satellite into orbit
Aug. 24, 2016: North Korea successfully launches a ballistic missile from a submarine
Sept. 5, 2016: North Korea fires three ballistic missiles about 1,000 kilometers, at least one of which entered Japan’s air defense zone
Sept. 9, 2016: North Korea conducts fifth nuclear test
Oct. 16, 2016: North Korea fires a ballistic missile that immediately explodes after launch
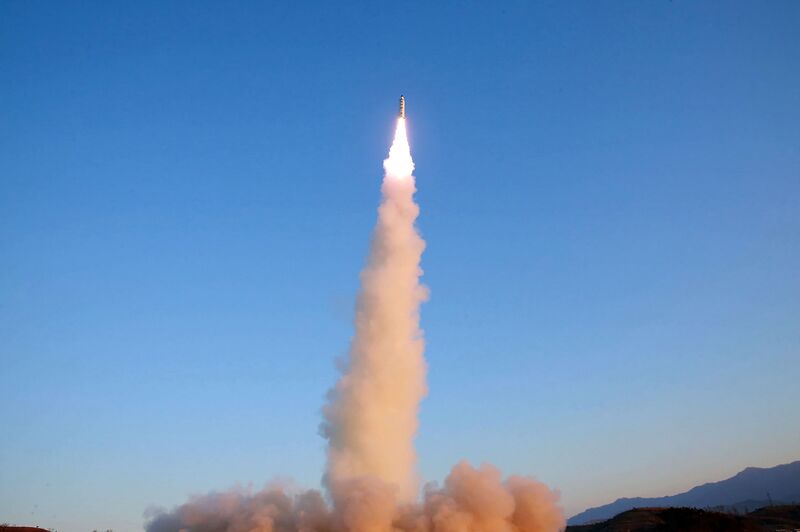

The launch of the Pukguksong-2 missile on Feb. 12.
Feb. 12, 2017: North Korea fires an intermediate-range Pukguksong-2 ballistic missile into nearby seas, drawing a joint rebuke from Trump and Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, who were meeting in Florida
March 6, 2017: North Korea fires four ballistic missiles, with three falling into Japan’s exclusive economic zone
April 16, 2017: North Korea fired an unidentified ballistic missile that exploded almost immediately after launch, defying warnings from the Trump administration to avoid any further provocations
Các bài viết khác
- 4 loại "rau trường thọ" mọc đầy ở Việt Nam (18.04.2017)
- Căn hộ 53 m2 kiêm văn phòng làm việc tại gia (17.04.2017)
- Ghi nhớ 5 điều Đức Đạt Lai Lạt Ma khuyên nhủ để cuộc sống khỏe mạnh, hạnh phúc cả về thể chất lẫn tinh thần (17.04.2017)
- Mua biệt thự 20 tỷ, đại gia "rung đùi" chờ tăng giá (17.04.2017)
- Đại gia đất Sài Gòn... vẫn nghèo (17.04.2017)
- Ăn theo hạ tầng, chung cư vừa túi tiền tiếp tục là "điểm nóng" trên thị trường (17.04.2017)
- "Không có chuyện dư thừa BĐS nghỉ dưỡng" (17.04.2017)
- HAVE WE ALREADY LOST THE SOUTH CHINA SEA? (17.04.2017)
- Recreating China’s Imagined Empire (17.04.2017)
- Tang poems and folk tales: Historys role in the Trump-Xi reset (17.04.2017)
- Giá nhà đất TP.HCM đang tăng mạnh, cảnh báo nguy cơ sốt ảo (17.04.2017)
- Vietnam: Evaluating Government Performance on its First Anniversary in Office (17.04.2017)
- Dân chung cư cũ sẽ vô cùng vui mừng khi biết thông tin này (17.04.2017)
- The Baby Boomer War (17.04.2017)
- Nỗi lo từ những cao ốc "mọc" trong hẻm (17.04.2017)
- The Modernization of the Vietnam Peoples Navy: Grand Goals and Limited Options (17.04.2017)
- Nạn kháng kháng sinh: kịch bản diệt vong! (12.04.2017)
- Thị trường căn hộ đầu năm: trầm lắng nhưng cân bằng (12.04.2017)
- Nhật ký đường về - Thơ Tố Hữu (10.04.2017)
- BĐS dịch chuyển sang phân khúc giá tầm trung (10.04.2017)
- Đề phòng sập bẫy nhà đất giá rẻ ở TP HCM (10.04.2017)
- Giao dịch bất động sản 2 tháng đầu năm giảm gần 40% so với cuối năm 2016 (10.04.2017)
- In Asias Infrastructure Race, Vietnam Is Among the Leaders (10.04.2017)
- The Crisis of Trumpism (10.04.2017)
- Tổng quan về thị trường bất động sản quý I/2017 (10.04.2017)
- Xuất hiện dấu hiệu đáng lo ngại với bất động sản (10.04.2017)
- M&A: Xu thế của thị trường BĐS Việt Nam (08.04.2017)
- Nhà đất tiếp tục tăng giá (08.04.2017)
- Dự án 3,5 tỷ USD giải ngân 96,5 tỷ đồng (08.04.2017)
- Cao ốc quá nhiều: Bất cập mang tên “đúng quy trình” (08.04.2017)
- Dân Sài Gòn từng ngày chờ thoát nạn quy hoạch “treo” (08.04.2017)
- Bài tập xoa bụng giúp sống lâu trăm tuổi của danh y Biển Thước (08.04.2017)
- Trump and Xi: Two Imposing Leaders With Clashing Agendas (08.04.2017)
- Sai lầm khi đổ “núi tiền” vào sửa chữa căn hộ bình dân (08.04.2017)
- Office-tel ở Đông Sài Gòn: Ngoại sỉ, nội lẻ (08.04.2017)
- Căn hộ officetel: một “ẩn số” về pháp lý (06.04.2017)
- Sung sướng vì đã tìm ra loại nước uống “rẻ tiền” giúp bệnh nhân UNG THƯ sống thêm 60 năm dù bác sĩ khẳng định không sống quá 20 ngày (06.04.2017)
- Những "ông già" trong làng bất động sản Việt (06.04.2017)
- The Real Reason America Lost the War in Vietnam: Japan (06.04.2017)
- Thị trường căn hộ trầm lắng (05.04.2017)
- 2 tháng đầu năm, vốn FDI vào bất động sản tăng gần 12 lần so với cùng kỳ năm 2016 (05.04.2017)
- Cuộc đua đầu tư căn hộ tầm trung (23.03.2017)
- Diễn biến “lạ” của thị trường địa ốc Hà Nội (23.03.2017)
- Doanh nghiệp địa ốc đua nhau hồi sinh dự án “trùm mền” (23.03.2017)
- Dự báo Future Timeline 2041-2046 (23.03.2017)
- Khách Nhật chuộng thuê căn hộ nhỏ tại Việt Nam (23.03.2017)
- Bẫy… Bất Động Sản (23.03.2017)
- Bị chiếm dụng trụ sở, hàng chục nhà khoa học "ra đường" (23.03.2017)
- Hậu liên doanh PTC - Arkins: Đẩy nhà khoa học ra đường (23.03.2017)
- Thủ tướng chỉ đạo "xử lý dứt điểm", vẫn nhùng nhằng (23.03.2017)
- Ngưng tách thửa đến bao giờ? (19.03.2017)
- TÌM THẤY CÂY THUỐC HIẾM TRỊ MỠ MÁU CAO, GAN NHIỄM MỠ, TĂNG HUYẾT ÁP TẠI VIỆT NAM (19.03.2017)
- TP.HCM có 1.151 dự án chậm triển khai (19.03.2017)
- Nghẹt thở với cao ốc (19.03.2017)
- Sôi động mua bán dự án bất động sản (19.03.2017)
- Báo Nhật: Mỹ phong tỏa đảo nhân tạo phi pháp Trung Quốc nguy cơ bùng phát chiến tranh (19.03.2017)
- 5 Thuốc Bổ Gan Uy Tín Trên Thị Trường (19.03.2017)
- Doanh nghiệp bắt tay có thể giảm 20% giá xây nhà (19.03.2017)
- Học giả Mỹ đề xuất 4 bước phá hủy đảo Trung Quốc xây trái phép ở Biển Đông (19.03.2017)
- Zombie Hordes: Thousands of Japanese Firms Dodging Bankruptcy (19.03.2017)
- Về mối liên thông giữa thị trường bất động sản, vốn và tiền tệ (10.03.2017)
- Bất động sản 201...: Ai sẽ “đứt gánh” giữa đường? (10.03.2017)
- Đột phá bởi từ trước đến nay BĐS nghỉ dưỡng chưa từng có chính sách cam kết lợi nhuận (10.03.2017)
- Hưng Thịnh sẵn sàng nguồn hàng kinh doanh trong 10 năm tới (10.03.2017)
- Life expectancy to reach 90 for the first time (10.03.2017)
- Những tuyến phố TPHCM có giá đất đắt khủng khiếp (10.03.2017)
- Khi nào bất động sản tăng và “nổ”? (10.03.2017)
- Một Nước Nhật Quá Xa Xôi (10.03.2017)
- Xì hơi hay vỡ bong bóng? (08.03.2017)
- Ẩn số khó lường về tồn kho bất động sản (08.03.2017)
- Chung cư tiền tỷ: Không có chuyện “trắng tay” sau 50 năm (08.03.2017)
- Đầu tư địa ốc Hà Nội khác Sài Gòn (08.03.2017)
- 7 điều kỳ diệu bất ngờ xảy ra với cơ thể khi bạn đi bộ mỗi ngày (08.03.2017)
- Báo Nga: Sẽ có thuốc trị tất cả các loại ung thư sau 3-4 năm nữa (08.03.2017)
- Doanh nghiệp địa ốc nổi tiếng tại TP. HCM đề xuất xây nhà giá dưới 150 triệu đồng (08.03.2017)
- Siết dần dòng vốn vào bất động sản (07.03.2017)
- Nhiều dự án “nổ” quá đà để bán nhà (07.03.2017)
- Người dân có bị "hớ" khi đang mua chung cư hiện nay? (07.03.2017)
- Không dễ hợp thức hóa nhà mua giấy tay (07.03.2017)
- Billionaire Lis Biotech Firm a Step Closer to Putting New Cancer Drug on Marke (07.03.2017)
- "Chúa đảo" Đào Hồng Tuyển: Đã chuẩn bị sẵn 20.000 tỷ tiền mặt, siêu dự án tại Tp.HCM sẽ có tổng mức đầu tư 65.000 tỷ (07.03.2017)
- 8 địa điểm phù hợp làm nhà giá 100-200 triệu ở TP HCM (03.03.2017)
- Chủ đầu tư PVC Land mở thủ tục phá sản, khách hàng như "ngồi trên đống lửa" (03.03.2017)
- TP.HCM làm đường vào khu tái định cư 38,4ha ở quận 2 (03.03.2017)
- TP.HCM xử lý 26 chung cư cũ trong năm 2017 (03.03.2017)
- Sài Gòn cần 1 triệu căn nhà giá rẻ trong thập kỷ tới (03.03.2017)
- Sài Gòn bùng nổ chung cư trong hẻm (03.03.2017)
- Sau một tháng thận hồi sinh hơn 20 tuổi! (03.03.2017)
- “Mừng quá các chị ơi, ba em nhờ uống loại cỏ dại này mà hết hẳn ung thư gan rồi đấy ạ!” (03.03.2017)
- Thị trường địa ốc cuối năm: “Náo loạn” chiết khấu giá bán căn hộ cao cấp (03.03.2017)
- Chuyên gia Phạm Chi Lan: ‘Bất động sản không thể làm chỗ dựa cho nền kinh tế’ (03.03.2017)
- Bài 121: Vị trí, công dụng, cách tập thở các loại Đan Điền (03.03.2017)
- Cách phục hồi gan do tác hại của rượu bia (03.03.2017)
- Nghịch lý thị trường căn hộ giá rẻ (03.03.2017)
- Kiến nghị bắt buộc đăng ký đất đai (03.03.2017)
- CBRE: cơ sở hạ tầng cần đi trước bất động sản (03.03.2017)
- Lấn cấn tính pháp lý của loại hình condotel (03.03.2017)
- Barack Obama Was a Foreign-Policy Failure (03.03.2017)
- 10 bí quyết sống khỏe của giáo sư Vạn Thừa Khuê: Càng biết sớm, bạn càng khỏe mạnh (03.03.2017)
- Trumpism and the Future of International Politics: The Return of Realism (03.03.2017)
- Trump as the New Andrew Jackson? Not on Old Hickory’s Life (03.03.2017)
- GIẢI ĐỘC GAN, TĂNG CƯỜNG CHỨC NĂNG GAN (03.03.2017)
- A Quarter of the Worlds GDP Is Undergoing Big Experiments (21.02.2017)
- Trumps foreign policy -- an elephant in a china shop? (21.02.2017)
- Why Chinas Creative Way to Fight Capital Outflows Wont Be Sustainable (21.02.2017)
- Cận cảnh khu đất 300ha tập đoàn VinGroup xây dựng khu đô thị VinCity đầu tiên tại TP.HCM (21.02.2017)
- China military official: War with US under Donald Trump becoming practical reality (21.02.2017)
- Cuộc đua của các đại gia địa ốc trên thị trường nhà ở TPHCM năm 2017 (21.02.2017)
- TPHCM: Khu phức hợp có tòa tháp cao nhất Việt Nam Empire City được tăng thêm gần 4.000 căn hộ (21.02.2017)
- The 30-Years War in Vietnam (21.02.2017)
- Thị trường dịch chuyển sang phân khúc nhà giá thấp (21.02.2017)
- Tillerson, Trump and the South China Sea (21.02.2017)
- These Countries Could Be Trump’s Next Trade War Targets (21.02.2017)
- Những “điểm nghẽn” đang kìm hãm thị trường BĐS (21.02.2017)
- Bất động sản và sự dịch chuyển phân khúc căn hộ giá “mềm” (17.02.2017)
- How America Can Take Control in the South China Sea (17.02.2017)
- Trump and China (17.02.2017)
- Donald Trump and the Coming Taiwan-China Crisis (17.02.2017)
- Mời học tiếng Anh bằng thơ lục bát (17.02.2017)
- TP.HCM có 1.151 dự án chậm triển khai (17.02.2017)
- Bài tập thở "để đời" giúp sống thọ và sống khỏe ai cũng nên biết (17.02.2017)
- Người mua nhà “tháo chạy” khỏi dự án vì “bước xuống đường là tắc” (17.02.2017)
- Ông Lê Khắc Hiệp: "Vingroup muốn thay đổi hoàn toàn quan niệm nhà giá rẻ là có chất lượng thấp" (17.02.2017)
- Chính sách Trump ở Biển Đông sáng dần qua “lăng kính” 3 nước ASEAN (17.02.2017)
- Bí thư Thăng “giật mình” với giá nhà xã hội 15 triệu/m2 (17.02.2017)
- Giám đốc Sở Xây dựng TP HCM bàn về nhà giá rẻ (17.02.2017)
- Cận cảnh khu nhà giá rẻ gần 2.000 căn hộ vắng bóng người tại huyện Bình Chánh (17.02.2017)
- 3 điểm nóng tăng giá đất mới năm 2017 tại TP HCM (07.02.2017)
- Noam Chomsky trên lịch sử dài của Mỹ can thiệp vào cuộc bầu cử nước ngoài (07.02.2017)
- Thế giới chúng ta đang sống là... giả lập?! (07.02.2017)
- Việt Nam và hoạt động quân sự ở Trường Sa (07.02.2017)
- Vì sao TQ triển khai hỏa tiễn ở Hoàng Sa? (07.02.2017)
- Vốn thu hẹp, bất động sản gặp khó? (07.02.2017)
- Thị trường bất động sản 2017: Có khả năng tụ “bong bóng”, sốt giá vào cuối năm? (07.02.2017)
- Thị trường bất động sản năm 2017 sẽ giảm nhiệt (07.02.2017)
- Đua nhau bán nhà trả chậm để kéo khách (07.02.2017)
- Thị trường địa ốc năm 2017 sẽ hạ nhiệt? (07.02.2017)
- “Mừng quá các chị ơi, ba em nhờ uống loại cỏ dại này mà hết hẳn ung thư gan rồi đấy ạ!” (07.02.2017)
- Lấn cấn tính pháp lý của loại hình condotel (07.02.2017)
- Hà Nội siết quy hoạch khu vực nội đô, căn hộ cao cấp càng đắt hàng (07.02.2017)
- Địa ốc Hoàng Quân: Lãi ròng quý IV/2016 giảm 12 lần (07.02.2017)
- TP.HCM điều chỉnh quy hoạch nhiều khu vực ở quận 3 (07.02.2017)
- Phong thủy năm Đinh Dậu 2017: Tháng 8, tháng 9 là thời điểm tốt để đầu tư vào bất động sản (07.02.2017)
- Công bố loại cây chữa khỏi ung thư có ở Việt Nam “mọc đầy mà chả ai biết” (07.02.2017)
- Phật dạy: 7 loại người chỉ nên bắt tay xã giao, tuyệt đối không kết bạn (06.02.2017)
- TP.HCM: Cuối năm BĐS cao cấp bán chậm, nhà vừa túi tiền 20 người tranh mua một căn (06.02.2017)
- Những người thích ở một mình thường có 5 đặc điểm "đáng gờm" sau! (06.02.2017)
- 6 lý do giá đất tiếp tục tăng năm 2017 (06.02.2017)
- Bất động sản 2016: Tác động của các chính sách lớn (06.02.2017)
- How China wins the South China Sea war without firing a shot (06.02.2017)
- 1967: The Era of Big Battles in Vietnam (06.02.2017)
- Wary of China, India offers Akash surface-to-air missile systems to Vietnam (06.02.2017)
- Tensions in the South China Sea National Intelligence Estimate: The Next Two to Three Years (26.01.2017)
- Stemming the Tide: Six Things China Can Do Next to Curb Outflows (26.01.2017)
- Ronald Reagan - A Time for Choosing (aka "The Speech") (26.01.2017)
- Reagan First State Of The Union Address January 26 1982 (26.01.2017)
- Peter Navarro is about to become one of the world’s most powerful economists (26.01.2017)
- The Reverse Kissinger (26.01.2017)
- Đảng Bảo thủ tán tỉnh với Trump sẽ kết thúc trong nước mắt (26.01.2017)
- Kinh doanh căn hộ siêu nhỏ ở New York (26.01.2017)
- Giá nhà ở Hồng Kông, Mumbai “chát” nhất thế giới (26.01.2017)
- From field to factory: Vietnams globalisation winners (26.01.2017)
- Can Donald Trump Avoid a Dangerous South China Sea Showdown? (26.01.2017)
- Bất động sản cao cấp liệu có tiếp tục tăng giá? (26.01.2017)
- Nhà thuộc diện cải tạo nhưng bỏ sót thì không quản lý (26.01.2017)
- Rủi ro kinh doanh bất động sản có thể tăng từ 150% lên 250% (23.01.2017)
- Vượt qua Hàn Quốc và Singapore, Nhật Bản chiếm ngôi đầu "săn mua" dự án BĐS Việt Nam (23.01.2017)
- Giá bất động sản hạng sang sẽ tăng vọt trong năm 2016? (23.01.2017)
- Bất động sản Việt Nam – thách thức nào sẽ đến trong năm 2017? (23.01.2017)
- Nhà mái tôn và mái gói đã lỗi thời, đây sẽ là xu hướng mới thịnh hành của tương lai (23.01.2017)
- Chủ đầu tư ăn bao nhiêu phần trăm lợi nhuận từ các dự án BĐS? (23.01.2017)
- Doanh nghiệp lao đao vì giá thuê đất tăng 7 lần (23.01.2017)
- 3 huyện ngoại thành TP HCM gần đủ tiêu chí lên quận (18.01.2017)
- U.S. May Put Some Big Weapons in the South China Sea (17.01.2017)
- Địa ốc 2011 - 2012 (17.01.2017)
- Bất động sản Tp.Hồ Chí Minh tiếp tục hút nhà đầu tư năm 2017? (17.01.2017)
- Cả trăm triệu đồng mỗi m2 căn hộ gần phố Wall Sài Gòn (17.01.2017)
- Ngắm ngôi nhà 3 tầng với những khu vườn nhỏ hút hồn ở TP. HCM (17.01.2017)
- Những thông tin này sẽ làm cho người mua nhà ngạc nhiên, bởi thị trường địa ốc năm 2017 sẽ đầy bất ngờ (17.01.2017)
- Free Market Fantasies: Capitalism in the Real World (17.01.2017)
- Vietnam Recalibrates After Trump-Duterte Combo Upsets Strategy (17.01.2017)
- WILL TRUMP LEAVE US TO CHINA’S MERCY, FRETS VIETNAM (17.01.2017)
- Thị trường bất động sản Việt Nam: Quy mô 21 tỷ USD, dư nợ 16 tỷ USD (17.01.2017)
- Địa ốc 24h: Vì sao giá đất TP.HCM năm 2016 cao gần gấp đôi năm 2015? (17.01.2017)
- Trumps troops prepare the ground for trade battles (17.01.2017)
- Thinking About a US-China War (17.01.2017)
- Four Futures: Life After Capitalism review – will robots bring utopia or terror? (17.01.2017)
- America: the failed state (17.01.2017)
- Bộ trưởng Xây dựng Phạm Hồng Hà: Sẽ siết quy hoạch đô thị (17.01.2017)
- TP.HCM bán đất công để tạo nguồn vốn phát triển hạ tầng (17.01.2017)
- Những thực phẩm giúp giảm axit trong dạ dày (16.01.2017)
- Thiết kế căn hộ chỉ 48 m2 nhưng thoải mái cho 4 người (16.01.2017)
- TPHCM thu hồi đất ở 6 quận cho tuyến metro Bến Thành - Tham Lương (16.01.2017)
- Đua nhau tung khuyến mãi để chèo kéo khách (15.01.2017)
- Những dự báo táo bạo cho thị trường bất động sản (14.01.2017)
- Căn hộ hạng sang sẽ tăng giá trong năm 2017 (14.01.2017)
- Mỹ Tàu vờn nhau và thế tam quốc ở Biển Đông (14.01.2017)
- Giá đất khu Cát Lái tăng 30% (14.01.2017)
- Tháo rào cản cho cơ chế quỹ đất 20% xây nhà ở xã hội (14.01.2017)
- Nhà giá rẻ còn rẻ nữa: Giữ chặt túi, đừng vội xuống tiền (14.01.2017)
- Quy hoạch là quy hoạch nào? (14.01.2017)
- Gia vị ngăn ngừa ung thư tuyến tụy (14.01.2017)
- Khốn khổ với những siêu dự án “trùm mền” (14.01.2017)
- TENSION AND RIVALRY IN INDOCHINA (14.01.2017)
- Nhà giá rẻ, “cuộc đua” ngày càng khốc liệt sau kế hoạch tỷ USD của Vingroup (14.01.2017)
- UPDATE 1 Vietnams 2016 inflation seen picking up, says World Bank (14.01.2017)
- Is Trump using Taiwan as a China bargaining chip? (14.01.2017)
- Chi tiết báo cáo của Hà Nội về dự án cao ốc Giảng Võ (13.01.2017)
- Đất nền các quận ven Sài Gòn có dấu hiệu tăng ảo (13.01.2017)
- Giá đất nền vùng ven TP.HCM tăng đến 40% so với năm trước (13.01.2017)
- Putin won 2016, but Russia has its limits as a superpower (12.01.2017)
- Russia Has Overcome Repression Before (12.01.2017)
- Bất động sản hết thời bấu víu vào “bầu sữa” tín dụng (12.01.2017)
- Báo cáo thị trường bất động sản: Sai số đáng báo động! (12.01.2017)
- Bằng cách làm này, từ công ty tí hon Novaland “lớn nhanh như thổi” thành ông lớn BĐS tỷ đô chỉ trong vài năm (12.01.2017)
- Tàu chiến Mỹ - Trung chạm trán gần Trường Sa (12.01.2017)
- Báo cáo chuyên đề đất đai (12.01.2017)
- Novaland tăng vốn điều lệ bốn lần trong năm 2016 (06.01.2017)
- Vingroup, Novaland, Vạn Thịnh Phát "dội bom" siêu dự án trên thị trường địa ốc TP.HCM (06.01.2017)
- Vốn FDI dần “tháo chạy” khỏi thị trường bất động sản Việt Nam? (06.01.2017)
- Địa ốc Hoàng Quân đầu tư thêm hàng loạt NƠXH (06.01.2017)
- Chuyên đề về bất động sản 2016 (06.01.2017)
- Bán nhà cho nợ 80%: Chiêu "đá" cục nợ xấu sang khách hàng? (06.01.2017)
- Biển Đông, Việt Nam đã đủ “đồ chơi” cần thiết! (06.01.2017)
- BĐS năm 2017: "Cú phanh bất ngờ" dưới tác động từ tín dụng ngân hàng? (06.01.2017)
- Bài toán kinh doanh bất động sản 2017 (06.01.2017)
- Thơ Việt Phương (06.01.2017)
- CHUYÊN ĐỀ Thị trường bất động sản 2008-2013 (06.01.2017)
- Tỳ vị yếu khó sống thọ: 4 bộ phận cơ thể báo hiệu tỳ vị của bạn suy yếu (01.01.2017)
- Bất động sản 2017 sẽ cạnh tranh một mất, một còn? (31.12.2016)
- Ồ ạt ưu đãi, tín dụng mua nhà… chững lại (30.12.2016)
- Chuyên gia Mỹ: Cảng Cam Ranh là chốt chặn chủ nghĩa bành trướng trên Biển Đông (30.12.2016)
- US against the world? Trump’s America and the new global order (30.12.2016)
- 5 dấu hiệu tố bạn bị gan nhiễm mỡ (30.12.2016)
- Phình to bong bóng bất động sản (30.12.2016)
- Bất động sản nghỉ dưỡng sống nhờ tiền ngân hàng (30.12.2016)
- Đun cà tím uống nước và đợi điều kì diệu xảy ra sau 2 ngày (30.12.2016)
- Tiền đổ vào bất động sản tăng mạnh dù thị trường chững lại (30.12.2016)
- Gót Asin của thị trường bất động sản 2016 (30.12.2016)
- 5 biến số tác động đến bất động sản TP HCM năm 2017 (30.12.2016)
- 4 yếu tố có thể kích bong bóng bất động sản (30.12.2016)
- TPP sẽ xoay chuyển bất động sản Việt Nam (30.12.2016)
- Thị trường bất động sản năm 2017 “nóng” hay “lạnh”? (30.12.2016)
- Năm 2017: Thị trường bất động sản cao cấp sẽ thoái trào? (29.12.2016)
- Khoảng 60.000 căn hộ đã được chào bán ra thị trường trong năm 2016 (29.12.2016)
- Nhiều cảnh báo cho thị trường bất động sản trong 2017 (29.12.2016)
- Nhà đầu cơ đang tạo sóng nhà đất (29.12.2016)
- Tại sao nhà phố thương mại River Park vừa ra hàng đã “sốt”? (29.12.2016)
- Welcome to the age of anger (29.12.2016)
- Làm giàu cần chậm mà chắc (29.12.2016)
- Nội soi dạ dày thực quản và những điều bạn nên chuẩn bị (29.12.2016)
- Thị trường căn hộ bình dân TP. Hồ Chí Minh tăng nhiệt (29.12.2016)
- Doanh nghiệp bất động sản lên kế hoạch gì cho năm 2017? (29.12.2016)
- Đô đốc Harry Harris: "Mỹ sẵn sàng đối đầu Trung Quốc ở Biển Đông" (29.12.2016)
- Bức tranh nào cho thị trường bất động sản 2017? (29.12.2016)
- Hơn 60.000 căn hộ tung ra thị trường Hà Nội, TP HCM năm 2016 (29.12.2016)
- How Singapores Not-Really-Rich Have Been Burned by Swiber Bonds (28.12.2016)
- How Singapore Beat New Zealand to Be Expats’ Top Place to Live (28.12.2016)
- “Cơn sốt” thị trường bất động sản Việt Nam – diễn biến nào tiếp theo? (28.12.2016)
- Giao dịch bất động sản cả năm sụt giảm (28.12.2016)
- ĐỘT PHÁ MỚI TRONG ĐIỀU TRỊ VIÊM GAN C MẠN NÂNG TỶ LỆ THÀNH CÔNG LÊN 93-99% (28.12.2016)
- Đó là thời gian để rác các mô hình kinh tế sai lầm mà làm cho thế giới thành một nơi nguy hiểm (28.12.2016)
- The Many Manipulations of Henry Kissinger (28.12.2016)
- Cam kết lợi nhuận khi mua Condotel chỉ là một kỹ thuật về tài chính (28.12.2016)
- Asia Embraces Bullet Trains as Singapore-Malaysia Deal Looms (28.12.2016)
- VỀ MỐI LIÊN THÔNG GIỮA THỊ TRƯỜNG BẤT ĐỘNG SẢN, VỐN VÀ TIỀN TỆ (28.12.2016)
- Tàu chiến Mỹ - Trung chạm trán gần Trường Sa (28.12.2016)
- Chuyên đề Địa ốc đóng băng 2006 (28.12.2016)
- Bob Kerrey và American Tragedy của Việt Nam (28.12.2016)
- Chuyên đề bất động sản năm 2011 (28.12.2016)
- War with China - Thinking Through the Unthinkable (28.12.2016)
- Viet Nam Drought and Saltwater Intrusion: Transitioning from Emergency to Recovery - Analysis Report and Policy Implications (17.12.2016)
- Sôi động nhà phố, đất nền khu Đông Tp.HCM (17.12.2016)
- Bất động sản: Khởi sắc cùng nỗi lo “bong bóng” (17.12.2016)
- “Ông lớn” bất động sản bắt đầu chuyển hướng (17.12.2016)
- Nietzsche was right – liberal democracy is flawed (17.12.2016)
- Phân biệt đau bụng dạ dày với các loại đau bụng khác (17.12.2016)
- “Sốt” như bất động sản nghỉ dưỡng biển Phú Quốc (17.12.2016)
- Thị trường BĐS: Cạnh tranh gay gắt trong phân khúc bình dân (17.12.2016)
- Thị trường BĐS Việt Nam 2017: Sự cân bằng lan tỏa trên các phân khúc (17.12.2016)
- TÌM HIỂU VỀ BỆNH VIÊM XUNG HUYẾT HANG VỊ DẠ DÀY (17.12.2016)
- Trung Quốc nên Chú ý đến bài học của Trân Châu Cảng (17.12.2016)
- Việt Nam bảo tố (Turbulence) trong Bất động sản & Xuất khẩu trong quý 3 năm 2016 (17.12.2016)
- Power and Order in the South China Sea (17.12.2016)
- Rise of the Robots Will Eliminate More Than 5 Million Jobs (17.12.2016)
- Robots Are Coming, But Not For Your Job (17.12.2016)
- Trump Says China Will Have to Play by Rules Under New Ambassador (17.12.2016)
- The real secret to Asian American success was not education (17.12.2016)
- The Crisis for Liberalism (17.12.2016)
- BĐS mở bán cuối năm: “Cháy hàng” hay sốt ảo? (17.12.2016)
- 10 Điều Khuyên “cho người cao niên” (17.12.2016)
- Đại gia địa ốc Sài Gòn đua mở rộng địa bàn để tranh thị phần mới (17.12.2016)
- Bất động sản tăng giá vào dịp cuối năm (17.12.2016)
- Lý do các tỷ phú thường dậy rất sớm (17.12.2016)
- Trump’s ‘Unpredictable Starting Now’ Foreign Policy Is Here (17.12.2016)
- Chapter 4 : TENSION AND RIVALRY IN INDOCHINA (17.12.2016)
- Loạt ảnh Full HD ‘nét căng’ về Sài Gòn 1967-1968 của John Beck (17.12.2016)
- Lỗ bạc tỷ vì buôn nhà phố nội thất hoành tráng (17.12.2016)
- Sẽ có thêm 8 ‘tháp’ chung cư ở khu Đông Sài Gòn (17.12.2016)
- Cơn sốt nhà xây sẵn lan rộng ở Sài Gòn (17.12.2016)
- Kịch bản nào cho thị trường địa ốc năm 2017? (17.12.2016)
- Cảnh báo dư thừa BĐS cao cấp, chuyên gia địa ốc nói gì? (17.12.2016)
- KCN Hiệp Phước TPHCM cho doanh nghiệp thuê đất diện tích nhỏ (17.12.2016)
- Cụ ông 4 lần tai biến, bệnh viện Mỹ trả về, sống sót thần kỳ nhờ lọ thuốc thời Lê (17.12.2016)
- Phó chủ tịch Cengroup: Với bất động sản đầu tư 10 dự án, thất bại chỉ 1 sẽ về tay trắng (17.12.2016)
- Thu hồi đất để làm 4 dự án ở quận 8 (17.12.2016)
- BỨC THƯ NỔI TIẾNG CỦA CHA GỬI CHO CON TRAI. (17.12.2016)
- Bùng nổ nguồn cung cuối năm, thị trường địa ốc phía Nam rất dễ bội thực (17.12.2016)
- Mua nhà khu vực nào ở TP.HCM để “thoát” ngập? (17.12.2016)
- Đất tăng giá chóng mặt, khách mua tiếc nuối (17.12.2016)
- Việt Nam chế tạo thành công phức hệ Nano FGC cho bệnh nhân ung bướu (17.12.2016)
- Những triệu chứng không ngờ báo trước bệnh ung thư từ 2 - 5 năm (17.12.2016)
- Dự án nhà ở phải được ngân hàng bảo lãnh (08.12.2016)
- Dự án bất động sản đổ dồn về quận 4 (08.12.2016)
- Hẻm sống (07.12.2016)
- Đà Nẵng: Thị trường căn hộ “nguội lạnh”, phân khúc khách sạn cao cấp tăng vọt (07.12.2016)
- How Stable Are Democracies? ‘Warning Signs Are Flashing Red’ (07.12.2016)
- How Trump Is Good for China (07.12.2016)
- Trump thắng cách nào? How Trump Won (07.12.2016)
- Diversity can distract us from economic inequality (07.12.2016)
- Donald Trump Vladimir Putin and the art of a deal with Russia (07.12.2016)
- Donald Trump Is a Curveball in Long Arc of US China Ties (07.12.2016)
- Kissinger: The View From Vietnam (07.12.2016)
- Is China ready to budge on the South China Sea? Here’s why compromise is possible (07.12.2016)
- Brexit No Barrier for Chinas New Financial District Plan in London (07.12.2016)
- Chinas Crony Capitalism: The Dynamics of Regime Decay, by Minxin Pei (07.12.2016)
- China’s brutally pragmatic response to a shifting world order (07.12.2016)
- China Deal Watch (07.12.2016)
- Căn hộ trung tâm TP.HCM thu hút khách hàng (07.12.2016)
- Can Global Capitalism Be Saved? (07.12.2016)
- Kỳ lạ: Cả huyện có tới 338 người sống thọ trên trăm tuổi nhờ một chất trong món ăn (07.12.2016)
- Lại lo bong bóng bất động sản (07.12.2016)
- Indias 007, Former Super Spy, Is Shaping Modis Foreign Policy (07.12.2016)
- Giao dịch nhà đất nhích lên (07.12.2016)
- Giá nhà đất: Thấy gì qua hai chiều tăng giảm? (07.12.2016)
- China-Vietnam agreement signals regional shift in the South China Sea (07.12.2016)
- China’s Great Leap Backward (07.12.2016)
- Henry A. Prunier, 91, U.S. Soldier Who Trained Vietnamese Troops, Dies (03.12.2016)
- Giải mã chính sách của Trump đối với châu Á (03.12.2016)
- Nhiều người không biết Lô hội là ‘báu vật’ vì 13 công dụng tuyệt vời này (03.12.2016)
- Căn hộ vùng ven tăng giá bán cuối năm (03.12.2016)
- Daewon tháo chạy, dự án khu đô thị 180ha ven biển Đà Nẵng về tay tập đoàn Novaland (03.12.2016)
- Mua nhà cho thuê - kênh đầu tư “hot” 2017? (03.12.2016)
- Kịch bản nào cho thị trường địa ốc năm 2017? (03.12.2016)
- Hạ tầng khu Đông kéo lượng giao dịch nhà liền kề TP.HCM đạt kỷ lục (03.12.2016)
- Ung thư gan giai đoạn cuối, bệnh viện trả về để “đóng quan tài”, bỗng chốc hồi sinh nhờ cà gai leo (03.12.2016)
- Phản hồi loạt bài “Hậu bong bóng bất động sản - Ai bảo vệ người dân? (03.12.2016)
- DÙ LÀ AI CŨNG NÊN ĐỌC BÀI NÀY, ĐỪNG ĐỂ GẦN ĐẤT XA TRỜI MỚI TIẾC ! (03.12.2016)
- Cả thế giới ăn mừng vì đã tìm ra loài hoa chống ung thư và kháng HIV cực mạnh rồi này (03.12.2016)
- Phát hiện lá CHỮA KHỎI UNG THƯ GIAI ĐOẠN CUỐI mọc đầy ở Việt Nam ít người biết (03.12.2016)
- Thần dược giết chết tế bào ung thư trong 10 ngày gây xôn xao thế giới (03.12.2016)
- Giao lưu trực tuyến Lưu ý khi mua nhà trong tương lai (27.11.2016)
- Ủy quyền nhà: Dễ rủi ro nếu không công chứng (27.11.2016)
- Giá nhà đất hong kong lao dốc do thay đổi chính sách (27.11.2016)
- Tiết lộ “sốc” về con số lợi nhuận của các dự án căn hộ cao cấp (27.11.2016)
- Tín dụng bất động sản: các ngân hàng đã siết (27.11.2016)
- Bài 1: Đóng tiền thật, được nhà ảo (27.11.2016)
- Phình to bong bóng bất động sản (27.11.2016)
- Loại bỏ quy hoạch kéo dài (27.11.2016)
- Trumps Win May Be Asias Loss (27.11.2016)
- Trumps challenge: Can he stop conflict in the South China Sea? (27.11.2016)
- The Clintons were undone by the middleAmerican voters they once knew so well (27.11.2016)
- VIỄN TƯỞNG (27.11.2016)
- Vietnam’s Stellar Economic Growth Stumbles (27.11.2016)
- Nhà đầu tư và người mua nhà đang hướng về Thủ Thiêm (16.11.2016)
- Nhiều nơi nhà đất tăng giá gấp 2-3 lần (16.11.2016)
- Những con số ấn tượng tại khu biệt thự Đông Sài Gòn (16.11.2016)
- Nở rộ bất động sản cao cấp, nên chọn dự án nào? (16.11.2016)
- Ông chủ Địa ốc Phát Đạt: "Kinh doanh chỉ cần thiên thời, địa lợi, nhân hòa chứ không cần cao nhân nào chỉ bảo" (16.11.2016)
- Rodrigo Duterte Gets Gần gũi hơn với Trung Quốc, và những người hàng xóm Chú ý (16.11.2016)
- Tiền thừa nhưng không dành cho bất động sản (16.11.2016)
- TP.HCM duyệt quy hoạch dự án Saigonres Riverside (16.11.2016)
- Trump đối diện với nhiều nền Kinh tế Rất khác nhau của Trung Quốc hơn tám năm trước (16.11.2016)
- Dự án “khủng” nhưng ít người biết của Tập đoàn Him Lam (16.11.2016)
- Đầu tư vào Condotel: Nếu không biết cách chơi, dễ “cầm dao đằng lưỡi” (16.11.2016)
- Why the Washington Visit of the Vietnam Communist Party Permanent Secretary is Critical (16.11.2016)
- What I Told My Kids About Trumps Election Today (16.11.2016)
- The Fatal Mistake That Doomed Samsung’s Galaxy Note (16.11.2016)
- The Clintons were undone by the middle-American voters they once knew so well (16.11.2016)
- Ngân hàng Trung ương Trung Quốc nhức đầu với Trump (16.11.2016)
- Lớn nhất Binge Bất động sản thế giới của Is Coming đến một thành phố gần bạn (16.11.2016)
- Thị trường đất nền phía Nam đang chuyển dịch mạnh (16.11.2016)
- Một số vấn đề đặt ra trong xử lý mối quan hệ giữa đổi mới chính trị và đổi mới kinh tế (16.11.2016)
- Lại lo bong bóng bất động sản (16.11.2016)
- Đất khu văn phòng gần trung tâm Sài Gòn 280 triệu đồng mỗi m2 (15.11.2016)
- Đây là mô hình ăn uống giúp người dân Nhật có tuổi thọ cao nhất thế giới (15.11.2016)
- Donald Trump is moving to the White House and liberals put him there (15.11.2016)
- Chiến lược và sách lược trong sự tham gia của Nga trong vùng biển Nam Trung Quốc 2016 (15.11.2016)
- CBRE sức tiêu thụ căn hộ trung cấp áp đảo trong quý 3 2016 (15.11.2016)
- Bất động sản Singapore xuống sát đáy hơn cả Hồng Kông, LaSalle nói (15.11.2016)
- BÌNH CHUẨN (1) THƯ - Sử Ký Tư Mã Thiên (15.11.2016)
- Những hòn đảo đẹp như cổ tich (19.09.2016)
- More Old Than Young A Demographic Shock Sweeps the Globe (19.09.2016)
- Đặc điểm ngoại hình dự báo bạn sống thọ hay chết sớm (19.09.2016)
- Trung Quốc nói đến thả lỏng Tổng hạn ngạch cho Thâm Quyến-Hồng Kông liên kết (19.09.2016)
- Billionaire Li KaShing Is Getting Back Into Hong Kong Housing Market (19.09.2016)
- GiÃN PHẾ QUẢN (19.09.2016)
- Bật mí cách “làm sạch” máu, hạ cholesterol trong 40 ngày (19.09.2016)
- Bác sĩ "thổi bay" ung thư phổi: Rảnh là thiền (19.09.2016)
- Thực hiện 7 điều này bạn sẽ làm việc thông minh và đỡ vất vả hơn (15.09.2016)
- Bài thuốc nam hay điều trị khỏi hẳn bệnh Suy Thận (15.09.2016)
- Những bài học về phép trường sinh của một người thọ 256 tuổi (15.09.2016)
- CHỊ NÓI CHO CHÚ BIẾT (14.09.2016)
- Bí quyết trường thọ năm Ất Mùi 2015 (14.09.2016)
- Beijing is on the back foot over the South China Sea dispute - America must act now (14.09.2016)
- Is a new cold war brewing over the South China Sea? (14.09.2016)
- Bài thuốc Nam đẩy lùi ung thư, u xơ gan, viêm gan (14.09.2016)
- Trung Quốc và “Kế hoạch tuyệt mật 861” dưới đáy Biển Đông (14.09.2016)
- PHILIPPINES DRUG WAR: DEATHS HAVE SPIKED SINCE DUTERTE BECAME PRESIDENT (14.09.2016)
- Billionaires 28-Year-Old Son Picks Digital Music Empire Over Palm-Oil Riches (14.09.2016)
- Hóa ra tay thường bị tê, chuột rút ở chân, kỳ thực là do các nội quan đang cố phát ra tín hiệu cầu cứu! 99% mọi người không biết, muộn biết thêm 1 giây có thể sẽ phải hối hận suốt quãng đời còn lại! (14.09.2016)
- Hiểu thêm về VN đưa EXTRA ra Biển Đông (26.08.2016)
- Một số ý kiến trao đổi về điều kiện hình thức của hợp đồng chuyển nhượng quyền sử dụng đất theo quy định của dự thảo Luật đất đai sửa đổi (26.08.2016)
- HENRY KISSINGER INTERVIEW WITH DER SPIEGELHenry Kissinger interview with Der Spiegle (26.08.2016)
- Thực hiện 7 điều này, bạn sẽ làm việc thông minh và đỡ vất vả hơn (26.08.2016)
- Trung Quốc Đã Bắt đầu giải cứu Ngân hàng (26.08.2016)
- trung Quốc có một núi nợ khổng lồ (26.08.2016)
- TƯƠNG LAI CỦA HỘI TỤ KINH TẾ (26.08.2016)
- How to Avoid War in the South China Sea (26.08.2016)
- Bốn quỹ bất động sản đóng băng gây hoảng loạn (26.08.2016)
- Oil Giants Find There’s Nowhere to Hide From Doomsday Market (26.08.2016)
- Các Yuan là tăng giảm một lần nữa, Nhưng ít được quan tâm (26.08.2016)
- Temasek Assets Likely Fell First Time Since 2008 on China Rout (26.08.2016)
- Vấn nạn truyền thông phần nổi của tảng băng chìm (26.08.2016)
- 9 lời tiên đoán cho nhân loại 100 năm tới (26.08.2016)
- 3 đặc điểm chung của những người trường thọ (26.08.2016)
- Hội chứng thiếu máu (26.08.2016)
- South China Sea Arbitration - Evolving Geopolitical Battle Lines Between China And US – Analysis (25.08.2016)
- Kịch bản nào cho thị trường bất động sản nửa cuối 2016? (25.07.2016)
- Những "thế lực" trong làng bất động sản (25.07.2016)
- TPHCM: Thừa căn hộ cao cấp, thiếu căn hộ bình dân (25.07.2016)
- TP.HCM: Số lượng biệt thự, nhà phố bán ra tăng kỷ lục (25.07.2016)
- Vì sao, thị trường căn hộ sức mua đang giảm (25.07.2016)
- When China and Vietnam Went to War: Four Lessons for History (25.07.2016)
- Lá Hen – thảo dược quý trong điều trị đờm – ho – khó thở (25.07.2016)
- Rối loạn nhịp tim (25.07.2016)
- Muốn phòng ung thư, hãy ăn khác người (25.07.2016)
- Viêm phế quản mạn điều trị thế nào? (25.07.2016)
- Kiến nghị tái định cư tại chỗ với cư dân ở chung cư cũ (25.07.2016)
- TPHCM: Sức mua căn hộ quí 2 giảm mạnh (25.07.2016)
- Cây Lá Hen (25.07.2016)
- Tiết Lộ Cây Thảo Mộc Qúy Chữa Dứt Điểm Bệnh Dạ Dày, viêm loét Đại Tràng,… sau 10ngày (25.07.2016)
- Dự báo quan trọng về Biển Đông sau phán quyết của Tòa (25.07.2016)
- 7 cách giữ sức khỏe và thân hình của người Nhật (04.07.2016)
- Why the US Rebalance to Asia Is More Important Than Ever (04.07.2016)
- Khó thở và các dấu hiệu chẩn đoán bệnh tim mạch (04.07.2016)
- Vũ trụ trung sinh (04.07.2016)
- Thời hiệu và thực tiễn áp dụng chế định thời hiệu trong lĩnh vực pháp luật dân sự. (04.07.2016)
- The Many Manipulations of Henry Kissinger (04.07.2016)
- China vs. America: Who Would Win the Battle of the South China Sea? (02.07.2016)
- Mời ngắm hoa, lạ và đẹp! (02.07.2016)
- George Soros said China (01.07.2016)
- More than 45 million trapped in modern slavery: Study (01.07.2016)
- Tomgram: Noam Chomsky Những thách thức của năm 2016 (01.07.2016)
- Dấu hiệu cảnh báo gan của bạn không khỏe (01.07.2016)
- Trung Quốc chính thức tuyên chiến ở Biển Đông? (01.07.2016)
- 10 giây để sống sót qua con đau tim khi chỉ ở một mình nhất định bạn phải nhớ (01.07.2016)
- Đây là thứ tiêu diệt tế bào ung thư mạnh mẽ gấp 10 nghìn lần thuốc hóa trị (01.07.2016)
- BÁO CÁO THỊ TRƯỜNG BẤT ĐỘNG SẢN VIỆT NAM QUÝ 1 2016 (06.06.2016)
- NHNN siết tín dụng BĐS nhẹ hơn dự kiến, liệu có hiện tượng tăng tốc rót vốn vào dự án? (06.06.2016)
- Hình thành cộng đồng dân cư - đỉnh cao của chiến lược đầu tư bất động sản (06.06.2016)
- (06.06.2016)
- TP.HCM: Cập nhật tiến độ chung cư giá rẻ T5/2016 (06.06.2016)
- “Cơn sốt” thị trường bất động sản Việt Nam – diễn biến nào tiếp theo? (06.06.2016)
- Chạy bộ mỗi sáng phòng ngừa ung thư (06.06.2016)
- Bất động sản: tăng trưởng nhưng tiềm ẩn rủi ro (06.06.2016)
- Sức hút Golf Park Residence với lịch thanh toán 0,5%/tháng (05.06.2016)
- Lộ diện những siêu kế hoạch làm "khuấy động" thị trường BĐS khu trung tâm TPHCM (05.06.2016)
- Những "nhóm đại gia" BĐS đang khuấy đảo thị trường địa ốc Sài Gòn (05.06.2016)
- Tế bào ung thư bị tiêu diệt trong 42 ngày bằng ly nước ép đã thành công ngoài mong đợi (05.06.2016)
- Thảo dược Triphala có tác dụng gì? (05.06.2016)
- Keppel Land tham gia dự án "chọc trời" ở Thủ Thiêm (05.06.2016)
- Hiểu biết ung thư để cứu mình (05.06.2016)
- Gần một nửa các dự án bất động sản tại TP.HCM đang “chết lâm sàng” (05.06.2016)
- South China Sea: Who Occupies What in the Spratlys? (05.06.2016)
- Các dự án cao cấp tại khu Đông TPHCM tiếp tục so kè tiến độ từng ngày (05.06.2016)
- Đau đầu thương lượng bồi thường đất (05.06.2016)
- 'Tận diệt' mọi tế bào ung thư chỉ với 4 muỗng hỗn hợp kì diệu này (05.06.2016)
- Thị trường bất động sản tiềm ẩn nhiều nguy cơ (05.06.2016)
- Biển Đông: Trung Quốc thúc ép quân đội "liều mạng" để chiến thắng (05.06.2016)
- Sự bứt tốc của thị trường địa ốc đang hụt hơi? (05.06.2016)
- Nam giới bắt đầu lão hóa từ tuổi nào (05.06.2016)
- Sức hút căn hộ đất vàng? (04.06.2016)
- Xử lý rối loạn tiêu hóa ở người già (09.05.2016)
- Dự án "khủng" 2,2 tỷ USD tại Khu Đô thị mới Thủ Thiêm sắp được khởi công (09.05.2016)
- Sở hữu chung cư có thời hạn - tại sao nên? (09.05.2016)
- Những phương thuốc cực rẻ, giúp nâng cao thể lực cho bạn. (09.05.2016)
- Tp.HCM: Hàng trăm dự án BĐS “chết lâm sàng” (08.05.2016)
- Gởi Các Bạn trên 60 Tuổi và còn Khỏe mạnh ( Hua Tham suu tam ) (08.05.2016)
- Doanh nhân này sở hữu hàng loạt BĐS độc đáo cả nghìn tỷ giữa Phú Mỹ Hưng (08.05.2016)
- Doanh nghiệp bất động sản như ngồi trên lửa (08.05.2016)
- Có triệu chứng này nghĩ ngay ung thư dạ dày (08.05.2016)
- ĐHCĐ Phát Đạt: Sớm trở lại đường đua với 7 lô đất lớn hơn 3.000 tỷ ở Thủ Thiêm (08.05.2016)
- Bàn cờ chiến lược tại Biển Đông (08.05.2016)
- Những lợi thế sức khỏe của tuổi già (08.05.2016)
- Khi các 'đại gia' xin chừa bất động sản (08.05.2016)
- Kéo dài tuổi thọ (08.05.2016)
- Doanh nghiệp bất động sản vẫn “sợ” lãi suất (08.05.2016)
- TS Lê Xuân Nghĩa: Điều bất ngờ của thị trường BĐS sẽ diễn ra vào năm 2019 (08.05.2016)
- Ngân hàng ngừng cho vay mua nhà dự án, thị trường BĐS sẽ ra sao? (08.05.2016)
- 5 năm nữa, mỗi người dân Hà Nội, TP.HCM... sẽ có 50m2 đất ở (08.05.2016)
- TPHCM: Giao dịch biệt thự - nhà phố giảm mạnh trong quý 1/2016 (08.05.2016)
- TƯƠNG LAI CỦA HỘI TỤ KINH TẾ * (08.05.2016)
- Vì sao người Hoa ở Macau sống thọ? (08.05.2016)
- Vietnam has a long history of conflict with its large neighbor to the north, China. (08.05.2016)
- Vincom mở rộng hệ thống tới Tây Nguyên và Nam Bộ (08.05.2016)
- Cảnh giác tín dụng bất động sản (08.05.2016)
- Sẽ xem xét thận trọng việc siết vốn vào bất động sản (07.05.2016)
- President Xi's allies taking pot shots at Premier Li's power base (07.05.2016)
- "Khát" căn hộ cao cấp cho thuê khu vực trung tâm TP.HCM (07.05.2016)
- Giáo sư đầu ngành "vạch mặt" nguyên nhân gây ra 80% ca ung thư (07.05.2016)
- Những tuyệt tác 'cổ lâm viên' Tô Châu, TQ (07.05.2016)
- "Giải nén" điểm nóng Biển Đông! (07.05.2016)
- Xác định thời điểm chuyển quyền sở hữu nhà ở và quyền sử dụng đất khi nhà ở và quyền sử dụng đất đều có giấy chứng nhận quyền sỡ hữu (07.05.2016)
- NHỮNG VƯỚNG MẮC KHI ÁP DỤNG NGHỊ QUYẾT 1037/2006/NQ-UBTVQH11 NGÀY 27-07-2006 CỦA UBTVQH VỀ GIẢI QUYẾT TRANH CHẤP NHÀ Ở CÓ YẾU TỐ NƯỚC NGOÀI. (07.05.2016)
- Khủng hoảng kinh tế, thi hành án cũng gặp khó 16-5-2012 (07.05.2016)
- Vũ khí Trung Quốc ở Hoàng Sa, Trường Sa nguy hiểm như thế nào đối với Việt Nam? (Phần 1) (07.05.2016)
- CÁCH PHÁT HIỆN SỚM UNG THƯ TRỰC TRÀNG (07.05.2016)
- Đâu chỉ BĐS “đau”, sao mỗi BĐS “khóc”… (07.05.2016)
- Người dân thay đổi quan điểm mua nhà, chung cư đang vào thời bùng nổ (07.05.2016)
- Hải ngoại huyết thư - Tục biên 海外血書-續編 • Bức thư bằng máu từ nước ngoài (07.05.2016)
- Tìm bất động sản hạng sang ở Quận 2 – dễ mà khó! (07.05.2016)
- Tòa án Quốc tế sẽ coi "đường lưỡi bò” của TQ là vô giá trị? (07.05.2016)
- Năng lượng tái tạo trên nhiên liệu hóa thạch như lớn nhất Nguồn New Power Hoa Kỳ (07.04.2016)
- Chủ tịch vương triều Tập có những điểm yếu của mình (07.04.2016)
- Postcapitalism : A Guide to Our Future by Paul Mason (07.04.2016)
- Chủ tịch VnREA: “Bất động sản phải được đối xử khéo léo và tế nhị” (07.04.2016)
- “Sao lại phải siết tín dụng vào bất động sản” (07.04.2016)
- Tập Cận Bình “Tôi biết làm thế nào?” (07.04.2016)
- Tín dụng BĐS trước nguy cơ “lửa cháy hai đầu”: “Liệu chúng ta có muốn lịch sử lặp lại?” (07.04.2016)
- Tổng hợp dự báo 2016 (07.04.2016)
- Top 5 Tech Predictions for 2025 BY JOHN BRANDON (07.04.2016)
- TPHCM duyệt dự án đầu tư bãi đậu xe ngầm Sân vận động Hoa Lư (07.04.2016)
- 1954, 1975, và những bài học không thể nào quên (07.04.2016)
- Tầm nhìn Lê Duẩn (07.04.2016)
- Vietnam moves from hyperinflation to zero (07.04.2016)
- The consequences of cheap oil (07.04.2016)
- Financial Times lý giải vì sao bây giờ là thời điểm tốt để mua bất động sản Việt Nam (07.04.2016)
- ĐỪNG ĐÁNH GIÁ THẤP VIỆT NAM (07.04.2016)
- Dự án tỷ đô trên đất vàng TPHCM thành bãi gửi xe, nuôi gà (07.04.2016)
- Biển Đông và chiến lược diều hâu của Trung Quốc (07.04.2016)
- Vietnam–US relations balancing ideology and geopolitics (07.04.2016)
- Con ở nhà cha mẹ là :HẠNH PHÚC, cha mẹ ở nhà con là : NHẪN NHỤC (07.04.2016)
- Người dân thay đổi quan điểm mua nhà, chung cư đang vào thời bùng nổ (07.04.2016)
- Chính sách kinh tế qua nghị quyết đại hội XII (07.04.2016)
- Chinese Diplomacy Towards Southeast Asia in 2014 (07.04.2016)
- China’s Major-Power Diplomacy (07.04.2016)
- BĐS vẫn thói nào tật đấy, ích kỷ và rất… tham lam (07.04.2016)
- Bất động sản Việt Nam sẽ tiếp tục bế tắc (07.04.2016)
- Bất động sản Việt Nam sẽ thu hút lượng vốn đầu tư cao kỷ lục từ châu Á (07.04.2016)
- At The Rolling Spring Roll in Syosset, Serving Vietnamese Classics (07.04.2016)
- 8 lý do khiến chung cư đang cho nhà mặt đất "ra rìa" (07.04.2016)
- 8 Loại rau ngăn ngừa 8 loại ung thư - 10 Lợi ích của trái XOÀI (07.04.2016)
- "Giải nén" điểm nóng Biển Đông! (07.04.2016)
- Hãy ăn 25 loại "siêu thực phẩm" này ngay lập tức (07.04.2016)
- Tiến độ loạt dự án căn hộ giá trên dưới 1 tỷ/căn tại TPHCM (07.04.2016)
- Lãnh đạo và cầm quyền (07.04.2016)
- Lột tẩy sự thật bán cắt lỗ chung cư sát Tết (07.04.2016)
- Mỹ, tên lửa triển khai của Trung Quốc là Chỉ bắt đầu (07.04.2016)
- Năm bứt phá của bất động sản (07.04.2016)
- Địa ốc Singapore phát triển thấp nhất trong 14 tháng qua (07.04.2016)
- Nhà giàu sợ nhất điều gì? (07.04.2016)
- Nhiều doanh nghiệp chuộng hình thức (07.04.2016)
- Những xu hướng nhà ở sẽ tăng tốc trong năm 2016 (07.04.2016)
- Nợ xấu BĐS: Nguy cơ trung hạn cho các ngân hàng (07.04.2016)
- Ông bố trẻ chi 16 triệu để làm vườn rau sạch cho vợ con (07.04.2016)
- TÌNH TRẠNG HỖN LOẠN VÔ CHÍNH PHỦ SẮP DIỄN RA TRÊN LỤC ĐỊA Á- ÂU (07.04.2016)
- Khống chế toàn cục Biển Đông, giấc mộng Tập Cận Bình sẽ thành công? (07.04.2016)
- Creed Group - Ẩn số lớn đến từ Nhật Bản (07.04.2016)
- Tổng quan dự án căn hộ Vinhomes Ba Son Quận 1 (07.04.2016)
- Boon for Vietnam properties (07.04.2016)
- Việt Nam và Hoàng Sa: Điều chỉnh đối sách ra sao để chống Trung Quốc? (07.04.2016)
- Thời đại hoàng kim của kháng sinh đã qua, trước mắt sẽ là cơn ác mộng với loài người (07.04.2016)
- Những xu hướng nhà ở sẽ tăng tốc trong năm 2016 (21.03.2016)
- Tham vọng của Trung Quốc ở Biển Đông (21.03.2016)
- CHINESE FALLACIES REGARDING THE SOUTHEAST ASIAN SEA (21.03.2016)
- Kỳ 2: Những kiến thức căn bản của khoa học làm giàu (21.03.2016)
- NHỮNG VƯỜN HOA ĐẸP NHẤT THẾ GIỚI (20.03.2016)
- Ông Nguyễn Văn Đực: “Vốn vào bất động sản nên chảy đúng chỗ” (20.03.2016)
- Quần đảo Trường Sa trong tầm nhìn địa chiến lược của Trung Quốc (20.03.2016)
- “Siết tín dụng bất động sản là một sai lầm“! (20.03.2016)
- Thị trường BĐS có nguy cơ "gục ngã" nếu thông tư 36 được sửa đổi (20.03.2016)
- Taking arms - The Asia-Pacific region is at peace—but it is buying a lot of weapons (20.03.2016)
- Tên lửa của tôi ở Biển Đông không phải là chuyện của ông (20.03.2016)
- Vietnam’s Submarine Fleet: What Impact on the South China Sea? (20.03.2016)
- Thị trường bất động sản sốt trở lại: Thật hay ảo? (20.03.2016)
- Tín dụng bất động sản trong vòng cương tỏa (20.03.2016)
- TP HCM dùng 7,37 tỷ USD vốn vay ODA để xây dựng 8 dự án (20.03.2016)
- Trung Quốc CÓ THỂ làm gì ở Biển Đông? (20.03.2016)
- Trung Quốc sẽ làm gì ở Biển Đông? (20.03.2016)
- U.S. Ready to Counter China’s Military Buildup: Carter (20.03.2016)
- Vay xấu vòng quanh thế giới (20.03.2016)
- Vietnam looks to state bank overhaul to stem NPL problem (20.03.2016)
- Vườn 'treo' thủy canh tại nhà (20.03.2016)
- World's Largest Energy Trader Sees a Decade of Low Oil Prices (20.03.2016)
- Người khôn ngoan sẽ đầu tư BĐS tại TPHCM trong năm 2016 (20.03.2016)
- Mỹ tên lửa triển khai của Trung Quốc là Chỉ bắt đầu (20.03.2016)
- Mỹ đã điểm huyệt TQ trên Biển Đông? (20.03.2016)
- moMoney Mo Vấn đề: The Rise of Wealth Therapy (20.03.2016)
- Lột tẩy sự thật bán cắt lỗ chung cư sát Tết (20.03.2016)
- Kiềm chế sự bành trướng của Trung Quốc (20.03.2016)
- Hiện Tượng Biển Tiến Trên Đất Việt (20.03.2016)
- The consequences of cheap oil (20.03.2016)
- Dự án 500 triệu USD bỏ hoang 11 năm, bí thư Đinh La Thăng ra "tối hậu thư" (20.03.2016)
- Điểm mới trong tranh chấp Biển Đông? (19.03.2016)
- Điểm lại mấy vấn đề then chốt sau Đại hội Đảng (19.03.2016)
- Death and Despair in China's Rustbelt (19.03.2016)
- Chính sách kinh tế qua nghị quyết đại hội XII (19.03.2016)
- Cận cảnh loài tre khổng lồ trên núi cao Quảng Nam (19.03.2016)
- Bí thư Đinh La Thăng hành động, sẽ có hàng trăm dự án BĐS tại Tp.HCM phải "toát mồ hôi"? (19.03.2016)
- Cuộc chiến Biển Đông đã bắt đầu! (19.03.2016)
- Thủ tướng Trung Quốc: Bắc Kinh sẽ chiếm Biển Đông! (19.03.2016)
- Chỉ 1 muỗng hạt đu đủ chữa lành bệnh xơ gan, viêm khớp và rất nhiều bệnh khác (19.03.2016)
- MINH TRIẾT VIỆT TRONG VĂN MINH ĐÔNG PHƯƠNG.15 (19.03.2016)
- Cha của Bill Gates dạy con như thế nào? (19.03.2016)
- Thật không ngờ làm thông mạch máu lại đơn giản như vậy! (19.03.2016)
- ĐẠO GIÁO & CHỬ ĐỒNG TỬ (19.03.2016)
- Cuộc chiến lâu dài của Đặng Tiểu Bình: xung đột quân sự giữa Trung Quốc và Việt Nam, 1979-1991 (The New Cold War History) (19.03.2016)
- Nguồn cung mất cân đối (19.03.2016)
- Muốn con lớn lên giàu có, nhất định phải dạy điều này (19.03.2016)
- Cảnh báo "bội thực" căn hộ cao cấp tại TP.HCM (19.03.2016)
- Bất động sản trước tác động từ việc sửa Thông tư 36 (18.03.2016)
- Tướng Cương: 'Trung Quốc đang xây tổ hợp quân sự ở Biển Đông' (18.03.2016)
- Chiến tranh Trung – Mỹ liệu có xảy ra? (18.03.2016)
- Thế trận mới ở Biển Đông (18.03.2016)
- Buôn nhà phố trong hẻm cụt lỗ cả trăm triệu đồng (18.03.2016)
- Ý tưởng “điên rồ”, đại gia BĐS Bitexco đang làm những thứ chẳng giống ai (18.03.2016)
- “Tuyệt chiêu” của người cha biến con trai mình từ một học sinh cá biệt thành sinh viên xuất sắc (18.03.2016)
- Lính Trung Quốc đóng dày đặc ở đảo Phú Lâm (18.03.2016)
- Điều gì xảy ra khi bạn ăn tỏi mỗi ngày? (18.03.2016)
- Bán nhà kèm cam kết cho thuê (18.03.2016)
- Duyệt văn phòng cho thuê, bán căn hộ để ở (18.03.2016)
- Bất động sản mô hình Officetel: Nửa nạc, nửa mỡ (18.03.2016)
- Doanh nhân 'cho thuê nhà 49 năm giá 350 triệu đồng' (18.03.2016)
- Bất ngờ với 10 lợi ích của việc đi bộ mỗi ngày (18.03.2016)
- Trung Quốc đối mặt nguy cơ bong bóng địa ốc (18.03.2016)
- 3 bài thuốc giảm cân đơn giản (18.03.2016)
- 4 kênh bất động sản tiềm năng năm Bính Thân (18.03.2016)
- 5 'cuộc cách mạng' trong y học (16.03.2016)
- 5 phương thức tín dụng đảm bảo ổn định thị trường BĐS (16.03.2016)
- Bán nhà kèm cam kết cho thuê (16.03.2016)
- MỘT CÁI NHÌN CỦA NGƯỜI TRONG CUỘC VỀ TRUNG QUỐC : QUÁ KHỨ VÀ TƯƠNG LAI. (16.03.2016)
- Hình ảnh 20 năm của BĐS (16.03.2016)
- Bất động sản không đóng băng! (16.03.2016)
- Bất động sản tăng trưởng nóng (16.03.2016)
- Bí thư Đinh La Thăng hành động, sẽ có hàng trăm dự án BĐS tại Tp.HCM phải "toát mồ hôi"? (16.03.2016)
- Bill Gates Q&A on Climate Change: ‘We Need a Miracle’ (16.03.2016)
- Các công ty của Trung Quốc có thể chinh phục thế giới? (16.03.2016)
- Chuyên đề về bất động sản 2016 (16.03.2016)
- Giá nhà 2016 sẽ biến động vì khả năng tăng lãi suất thời gian tới (15.02.2016)
- Đầu tư bất động sản nghỉ dưỡng: Đổ tiền mua lấy rủi ro? (15.02.2016)
- “Bệ phóng” cho bất động sản nghỉ dưỡng Phú Quốc (15.02.2016)
- Đầu năm “xông đất” các đại gia về đất (15.02.2016)
- Tăng kiểm soát rủi ro cho vay bất động sản (15.02.2016)
- Chủ doanh nghiệp địa ốc sợ thị trường nóng sốt (15.02.2016)
- Mỹ có thông điệp cho Việt Nam qua vụ tuần tra đảo Tri Tôn, Hoàng Sa? (15.02.2016)
- Tiết lộ động trời về trái mãng cầu xiêm, mọi người nên đọc ngay (15.02.2016)
- Địa ốc 24h: Nóng bỏng cuộc đua săn mặt bằng bán lẻ ở trung tâm Sài Gòn (15.02.2016)
- Bất động sản Sun Group gây ấn tượng tại Singapore (15.02.2016)
- Tôi đã thoát khỏi nỗi khổ đờm, ho, khó thở (15.02.2016)
- Nếu ngân hàng ngưng cho vay mua nhà, thị trường sẽ bị tác động rất lớn (15.02.2016)
- “Bất động sản là kênh đầu tư khá hấp dẫn trong năm 2016“ (15.02.2016)
- 5 'cuộc cách mạng' trong y học (15.02.2016)
- Doanh nhân 'cho thuê nhà 49 năm giá 350 triệu đồng' (15.02.2016)
- Bính Thân 2016: Tuổi nào hợp với nghề “buôn” bất động sản? (15.02.2016)
- Khoa học đã giải thích được ”ung thư là do nghiệp chướng“ (15.02.2016)
- Mỹ khiến Trung Quốc như “kiến bò chảo” với lá chắn tên lửa (15.02.2016)
- TPHCM tổ chức đấu giá 23 khu “đất vàng” (15.02.2016)
- Dưỡng Huyết Tiêu Phong Thang (22.01.2016)
- Nhặt chiếc nhẫn rơi - Câu chuyện cổ tích giữa đời thường (22.01.2016)
- Tuổi già hạnh phúc với nguyên tắc “5 không” (22.01.2016)
- Unthinkable: If America Walked Away from Asia (22.01.2016)
- The Many Manipulations of Henry Kissinger (22.01.2016)
- TÁC GIẢ DAVID ELLIOTT NÓI VỀ ĐÓNG GÓP CỦA CUỐN “BÊN THẮNG CUỘC” (22.01.2016)
- State-owned companies face new reforms (22.01.2016)
- Mời ngắm hoa, lạ và đẹp! (22.01.2016)
- Bí ẩn bức tượng Phật 4 lần rơi lệ ở Trung Quốc (06.01.2016)
- Top 15 “địa chỉ vàng” nhất định phải đến khi lạc sang quận Phú Nhuận (06.01.2016)
- TẠI SAO VIÊM LOÉT DẠ DÀY LẠI KHÓ CHỮA, HAY TÁI PHÁT? (06.01.2016)
- TPHCM chấp thuận đầu tư hàng loạt dự án nghìn tỷ (06.01.2016)
- Bất động sản 2016 chưa hẳn màu hồng (06.01.2016)
- War of words over South China Sea militarization heats up (06.01.2016)
- Việt Nam 'chuẩn bị đương đầu với TQ' (06.01.2016)
- Vì sao dự án BĐS tại TPHCM ngưng thi công tăng mạnh? (06.01.2016)
- Trường An: Kinh đô của 10 triều đại Trung Hoa (06.01.2016)
- THUỐC CHỮA TRỊ BỆNH TRÀO NGƯỢC DẠ DÀY THỰC QUẢN (06.01.2016)
- Thị trường bất động sản có dấu hiệu thổi giá (06.01.2016)
- Những ngón nghề “hốt bạc” từ bất động sản (P2) (06.01.2016)
- Người già, đôi chân già trước - Lợi ích của đi bộ (06.01.2016)
- ASIA'S GAME OF THRONES (06.01.2016)
- A China-Vietnam Military Clash (06.01.2016)
- How I Escaped Vietnam (06.01.2016)
- Hen phế quản (06.01.2016)
- DUY TRÌ SỨC KHỎE CÁC VỊ CAO NIÊN (06.01.2016)
- Chuyên đề Mỹ áp sát các đảo cát do Trung Quốc xây bất hợp pháp ở Biển Đông (06.01.2016)
- China’s Institutional Challenge (06.01.2016)
- Câu chuyện đời tôi - LÀM VIỆC VỚI CÁC NHÂN VẬT DANH TIẾNG THẾ GIỚI (06.01.2016)
- CÀ DÁI DÊ (06.01.2016)
- Bí quyết làm cuộc sống dễ chịu hơn (06.01.2016)
- Bạch Truật- vị thuốc quý của các vị đế vương (06.01.2016)
- "Bừng sáng" khu đô thị Sala Thủ Thiêm Quận 2 (06.01.2016)
- Khảo sát về Pháp Luân Công: Hiệu quả chữa bệnh và nâng cao sức khỏe lên tới 97,9% (06.12.2015)
- 100 lời khuyên lúc lâm chung của thần y 112 tuổi (phần 1) (06.12.2015)
- Hoàng liên (06.12.2015)
- Crying over cheap milk (06.12.2015)
- Vladimir Putin 2015 (06.12.2015)
- Việt Nam tìm kiếm các công cụ mới để x ử l ý khủng hoảng nợ xấu,nh ìn v ào thị trường kiểu Trung Quốc (06.12.2015)
- Trào ngược dạ dày thực quản và bệnh hen (06.12.2015)
- ASIA'S GAME OF THRONES (06.12.2015)
- DUY TRÌ SỨC KHỎE CÁC VỊ CAO NIÊN (05.12.2015)
- Cơ sở lý luận và thực tiễn nghiên cứu thời kỳ quá độ lên chủ nghĩa xã hội, bỏ qua chế độ tư bản chủ nghĩa ở Việt Nam hiện nay (05.12.2015)
- Chuyên đề Mỹ áp sát các đảo cát do Trung Quốc xây bất hợp pháp ở Biển Đông (05.12.2015)
- Câu chuyện đời tôi - Nguyễn Hữu Hanh (05.12.2015)
- Đau đại tràng, chữa đau đại tràng bằng thuốc nam hiệu quả (05.12.2015)
- Bộ tưới phun sương tự động trọn gói cho khu vườn có kích thước 84m2 (03.12.2015)
- Biocentrism / Robert Lanza’s Theory of Everything (03.12.2015)
- Bí quyết làm cuộc sống dễ chịu hơn (03.12.2015)
- Bạch Truật- vị thuốc quý của các vị đế vương (03.12.2015)
- 2019 timeline contents (03.12.2015)
- 2018 timeline contents (03.12.2015)
- 2017 timeline contents (03.12.2015)
- 2016 timeline contents (03.12.2015)
- Hồ sơ mật Những người kiến tạo nước Mỹ Phần 1 (13.11.2015)
- MiG 35 Russia's Answer to the F 35 (13.11.2015)
- Sống để làm gì - TT. Thích Chân Quang (13.11.2015)
- Tổng hợp vũ khí hiện đại Việt Nam đã nhận 2015 (13.11.2015)
- Tu 160 ' White Swan '! Wings of Russia (13.11.2015)
- Video việc Trung Quốc đang xâm chiếm và xây dựng trái phép ở Biển Đông phần 2 (13.11.2015)
- VTC14 Tìm thấy dấu vết mới của sự sống trên sao Hỏa (13.11.2015)
- White swan TU 160 (13.11.2015)
- Wings of Russia. MiG-25 and MiG-31. Best In Class (1 of 2) (13.11.2015)
- Why Quantum Physics Ends the Free Will Debate (13.11.2015)
- Welcome to the 2030s Future Timeline Events 2030 2039 (13.11.2015)
- Welcome to the 2020s Future Timeline Events 2020 2029 (13.11.2015)
- Những hình ảnh từ Sao Hỏa khiến thế giới phải kinh hoàng (13.11.2015)
- Sáng chế robot thay con người làm việc nhàm chán, nguy hiểm (13.11.2015)
- Phỏng vấn Chủ tịch Hiệp hội Thủy sản Mỹ Nguồn VTV (13.11.2015)
- Robot vận tải của Thủy quân lục chiến Mỹ (13.11.2015)
- Xi Jinping: A 21st-century Mao? (13.11.2015)
- Worst Idea Ever: Dropping Nuclear Bombs During the Vietnam War (13.11.2015)
- Will South China Sea Dispute Lead to World War? (13.11.2015)
- Why the United States and Vietnam Urgently Need to Deepen Ties (13.11.2015)
- Why NAFTA passed and the Trans-Pacific Partnership failed (13.11.2015)
- What it will take for a head transplant to work (13.11.2015)
- What is civic capitalism? An interview with Colin Hay (13.11.2015)
- What China dangerously underestimates about America's interest in the South China Sea (13.11.2015)
- What Caused capitalism? (13.11.2015)
- Weaponized The "China Card" Makes Its Return to U.S. Politics (13.11.2015)
- We have heard that the Secretary General of the Vietnam Communist Party (13.11.2015)
- Vladimir Putin 2015 (13.11.2015)
- Vietnam Muddles China's South China Sea Challenge (13.11.2015)
- Vietnam 40 Years Later (13.11.2015)
- Việt Nam đang ngồi nhìn? (13.11.2015)
- Với TPP Việt Nam sẽ trở thành cường quốc hàng hải 2030 (13.11.2015)
- Vì sao căn hộ nhỏ ở đô thị đang là mốt? (13.11.2015)
- U.S. to Vietnam: Stop Hosting Putin’s Jets Please (13.11.2015)
- US to Press China on Island Expansions (13.11.2015)
- Turf wars Vietnam s land rights crisis (13.11.2015)
- Tuổi Già Hải Ngoại Và Niềm Vui Internet (13.11.2015)
- TƯ BẢN Thế kỷ XXI (13.11.2015)
- Trung Xô luận chiến công khai (13.11.2015)
- Trung Quốc cưỡng chiếm trái phép Hoàng Sa (13.11.2015)
- Vị thế của Mỹ đang bị thách thức (12.11.2015)
- Tranh giành Quyền lực và Hòa giải Dân tộc (12.11.2015)
- TPHCM: Nguồn cung căn hộ tăng mạnh trong quý 3/2015 (12.11.2015)
- Tinh dầu thông đỏ chữa ung thư: Thần dược hay lừa đảo (12.11.2015)
- Tiền vẫn đổ vào bất động sản Hà Nội (12.11.2015)
- Thời sự và suy ngẫm, số 97 (12.11.2015)
- Thế nào là tướng có phúc khí? (12.11.2015)
- The Bloodthirsty Deng We Didn’t Know (10.11.2015)
- Tình hình 2011 và Ba kịch bản cho thị trường bất động sản đến cuối năm (10.11.2015)
- SECRETARY KISSINGER (10.11.2015)
- PHỐ ĐÔNG VILLAGE BIỆT THỰ, NHÀ PHỐ TỐT NHẤT TP. HCM, KĐT (10.11.2015)
- TPHCM khai thác nhà xưởng cao tầng đầu tiên (10.11.2015)
- Ông chủ Sơn Kim Land: Kinh doanh căn hộ cao cấp cũng giống như ngành thời trang (10.11.2015)
- Áo dài người Việt (09.11.2015)
- Chủ tịch vương triều Tập có những điểm yếu của mình (09.11.2015)
- Những thế cờ Hoa Kỳ - Trung quốc (09.11.2015)
- Nhật đang đổ bộ đầu tư vào bất động sản Việt Nam (09.11.2015)
- NGƯỜI MÊ PHỞ NÓI CHUYỆN PHỞ...! (09.11.2015)
- Ngập lụt đô thị - phải làm gì bây giờ? (09.11.2015)
- Năm năm nhìn lại chuyên đề tiền tệ 2011 (09.11.2015)
- Doanh nghiệp bất động sản như ngồi trên lửa (09.11.2015)
- Mỹ so với Trung Quốc: Chiến tranh là không thể tránh khỏi, chỉ cần? (09.11.2015)
- MÙA ĐÔNG ĐẾN SỚM VÀ NHẬT BẢN VỀ ĐÊM (09.11.2015)
- MUA BÁN NHÀ KHÔNG THÀNH XỬ LÍ RA SAO? (09.11.2015)
- 'Khó thay đổi lớn về chính trị ở VN' (09.11.2015)
- Hiểm họa Trung Quốc và bài học từ Tiệp Khắc, Ukraina (09.11.2015)
- Giá bất động sản - sự phi lý trong cái hợp lý (09.11.2015)
- Giá bán căn hộ tại TPHCM và Hà Nội quý 4/2015 vẫn khó (09.11.2015)
- Về giải quyết tranh chấp, khiếu nại, tố cáo về đất đai (09.11.2015)
- Dự báo 20 năm ( 2014-2034) (09.11.2015)
- Dự án Đảo Kim Cương đã bán được hơn 60% căn hộ (09.11.2015)
- Doanh nghiệp bất động sản như ngồi trên lửa (09.11.2015)
- Col Liu Mingfu on the U.S. and China as Rivals (09.11.2015)
- Chuẩn bị chiến tranh với Trung Quốc (09.11.2015)
- Chủ quyền Hoàng Sa – Trường Sa? (09.11.2015)
- Chủ nghĩa tư bản và khủng hoảng tài chánh toàn cầu Vietsciences- Nguyễn Trường (09.11.2015)
- China Stands by Its Claims Over South China Sea Reefs (09.11.2015)
- China’s South China Sea strategy: simply brilliant (09.11.2015)
- Can China Be Contained? (09.11.2015)
- Bong bóng bất động sản rất dễ xảy ra? (09.11.2015)
- Bill Gates: Nếu bạn nghĩ giáo viên của mình quá khó tính, bạn sẽ gặp trở ngại với cấp trên sau này (09.11.2015)
- BĐS dành cho nhà giàu bước vào cuộc đua mới (09.11.2015)
- Bào Chữa Vụ Án Lập quỹ trái phép phép tại Nông trường Sông Hậu (09.11.2015)
- Bài thuốc Minh Mạng thang gồm 22 vị (09.11.2015)
- Bài thuốc chống suy nhược từ linh chi (09.11.2015)
- Ảo Vọng Mùa Thu (09.11.2015)
- 2014Thị trường bất động sản đã trải qua nhiều thăng trầm (09.11.2015)
- 16 trường đại học đẹp nhất trên thế giới (09.11.2015)
- 7 tuần lễ sau khi thành đạo (08.11.2015)
- Chuyên đề Mỹ áp sát các đảo cát do Trung Quốc xây bất hợp pháp ở Biển Đông (28.10.2015)
- AFTER THE FALL OF SAIGON (27.10.2015)
- What Caused Capitalism? (27.10.2015)
- Cơ Hội Lớn Cho “Bánh Mì” Việt Nam (25.10.2015)
- HỒI KÝ TỪ TUỔI NGỦ THẬP ĐẾN THẤT THẬP CỦA PHẬT TỬ NGUYỄN KIM TOÀN (24.10.2015)
- Nhật Bản - Đất nước - Con người (08.10.2015)
- Nhạc không lời êm đềm du dương hay nhất sốt mọi thời đại Toinoi com (08.10.2015)
- Westlife When You Tell Me That You Love Me Wit (08.10.2015)
- Rachael Yamagata Over And Over Lyrics (08.10.2015)
- Over and Over Nana Mouskouri lyrics (08.10.2015)
- HD Chuc Xuan Ban AVT (08.10.2015)
- Nana Mouskouri Love Story (08.10.2015)
- John Legend - Tonight (Best You Ever Had) feat. Ludacris (08.10.2015)
- 1000 cụm từ tiếng anh thông dụng nhất hay sử dụng hàng ngày full (08.10.2015)
- LOVE STORY With Lyrics = ENGELBERT HUMPERDINCK (08.10.2015)
- LOVE STORY Where Do I Begin Andy Williams Ly (08.10.2015)
- Liệu có xảy ra xung đột quân sự ở Biển Đông (08.10.2015)
- Andy Williams, 20 Greatest Songs Hits with Lyrics 1 of 2 (08.10.2015)
- Full 5 Bước Để Nói Một Ngoại Ngữ YouTube (08.10.2015)
- Elton John SACRIFICE Lyrics HQ (08.10.2015)
- Ban kích động nhạc Số Dzách & AVT Thập niên 60 (08.10.2015)
- Creed My Sacrifice With Lyrics (08.10.2015)
- Ban AVT Chúc tết hải ngoại Clip giải trí hài kị (08.10.2015)
- Amazing Grace Best Version By Far! (08.10.2015)
- Amazing Grace Lyrics (08.10.2015)
- { Nana Mouskouri } Love Story (08.10.2015)
- 27 năm sự kiện Trung Quốc tấn chiếm Gạc Ma (08.10.2015)
- Hồ sơ mật Những người kiến tạo nước Mỹ Phần 1 (08.10.2015)
- Học qua bài hát (08.10.2015)
- Phát âm tiếng anh - Mr Kenny Ng (08.10.2015)
- Quan hệ Việt-Mỹ và thế cân bằng trong quan hệ với các siêu cường (08.10.2015)
- QUY HOẠCH SÀI GÒN TRƯỚC 1975 DƯỚI ẢNH HƯỞNG CỦA HOA KỲ (08.10.2015)
- Quyền lực dầu đá phiến Mỹ: Đòn khí đốt Nga vô hiệu (08.10.2015)
- Rối loạn kinh tế TQ và ảnh hưởng tới VN (08.10.2015)
- Sáu vấn đề đằng sau vụ chứng khoán TQ (08.10.2015)
- Tập Cận Bình (08.10.2015)
- Tham vọng quyền lực và sự tha hóa (08.10.2015)
- Thế chiến II: trại tù kinh hoàng của quân Nhật (08.10.2015)
- Thế giới không còn phẳng nữa rồi? (08.10.2015)
- Thế lưỡng nan của Hoàng đế Tập Cận Bình (08.10.2015)
- Lần theo dấu chân Người trên đất Mỹ - Bài 3: Bác Hồ ở Boston (08.10.2015)
- THUYẾT "LÃNH ĐẠO TỪ PHÍA SAU" HAY TRÒ "XUỴT CHÓ BỤI RẬM" (08.10.2015)
- Tìm lối ra cho kinh tế Việt Nam - Kỳ 12: Tái cơ cấu một cách đồng bộ (08.10.2015)
- Toàn văn chiến lược quân sự mới của Mỹ (08.10.2015)
- Tôi thực sự choáng trước dự thảo ‘sặc mùi Mỹ’ (08.10.2015)
- Tỷ phú số một Hồng Kông lặng lẽ rút khỏi Trung Quốc (08.10.2015)
- Vấn nạn Giáo dục Nguyên nhân và Hậu quả - Nguyễn Quang Dy (08.10.2015)
- (08.10.2015)
- Những điều lạ trong dự báo thế giới 100 năm tới - NGUYỄN HẢI HOÀNH (08.10.2015)
- Nhật Bản: ‘Thuế ở VN phức tạp, mất thì giờ’ (08.10.2015)
- Người dựng kỳ đài Ngày Độc lập 2/9 (08.10.2015)
- Nắm hàng triệu ha đất, nộp ngân sách không bằng một nhà máy (08.10.2015)
- Mỹ-Hoa và chiến lược dài hạn tại Thái Bình Dương (08.10.2015)
- Một số vấn đề kinh tế Trung Quốc đang đối mặt (08.10.2015)
- Li Ka Shing, tỷ phú "siêu nhân" (08.10.2015)
- Lá thư viết vào năm 2070... (08.10.2015)
- Lá thư để lại giữa rừng (08.10.2015)
- Kinh tế TQ qua các con số chóng mặt (08.10.2015)
- Hệ thống tài chính Việt Nam bị đánh giá rủi ro ở mức (08.10.2015)
- Hai mươi năm bức thư của cố Thủ tướng Võ văn Kiệt (08.10.2015)
- ĐỪNG CÓ DẠI, ĐẢNG CSVN KHÔNG QUÊN "CHUYÊN CHÍNH VÔ SẢN" ĐÂU. (08.10.2015)
- Ðời là bể khổ....Qua được bể khổ... là qua đời ! (08.10.2015)
- ĐỌC LẠI HỒI KÝ TRẦN QUANG CƠ (08.10.2015)
- Định nghĩa mới về kinh tế thị trường XHCN (08.10.2015)
- Diễn Văn Của Đức Giáo Hoàng Phanxicô tại Bolivia với Các Phong Trào Bình Dân (08.10.2015)
- Đảng CS lấy ý kiến về báo cáo chính trị (08.10.2015)
- Vấn nạn lớn nhất của Obama trong việc thúc đẩy TPP (08.10.2015)
- Việt Nam có thể trở thành một trong cửu bá trong thế giới đa cực vào năm 2025 (08.10.2015)
- Hệ thống ngân hàng (08.10.2015)
- The root of China's economic troubles? It's politics, stupid (08.10.2015)
- The Meaning of Kissinger (08.10.2015)
- henry Kissinger was 26 years old when he wrote a nearly 400 (08.10.2015)
- Interview With Chinese President Xi Jinping WALL STREET JOURNAL (08.10.2015)
- Đại sứ Lê Văn Bàng: Sự tham gia của Nhật sẽ tạo thế cân bằng ở Biển Đông (08.10.2015)
- Có hay không sự tồn tại của 'vùng cấm chính trị'? (08.10.2015)
- China’s risky money game (08.10.2015)
- Cải cách kinh tế thúc đẩy thay đổi thể chế (08.10.2015)
- Bức tranh toàn diện về xử lý nợ xấu ngân hàng từ 2010 đến tháng 8/2015 (08.10.2015)
- Báo cáo 2035: VN bị thách thức về kinh tế, dồn ép về xã hội (08.10.2015)
- Bài học dạy con làm nức lòng dân mạng của MC Nguyễn Cao Kỳ Duyên (08.10.2015)
- Dreams of Empire - PETER BERGER (08.10.2015)
- Việt nam trở thành công xưởng sản xuất khổng lồ của thế giới (08.10.2015)
- CURRENT HISTORY • September 2015 (08.10.2015)
- Bác Hồ đã chọn đúng những vị trí lãnh đạo (08.10.2015)
- Ba lý do khiến FED giữ nguyên lãi suất (08.10.2015)
- 2015.09-Gerwin_TPP-and-the-Benefits-of-Freer-Trade-for-Vietnam (08.10.2015)
- 16 trường đại học đẹp nhất trên thế giới (08.10.2015)
- 9 thứ người giàu nghĩ và hành động khác người nghèo (08.10.2015)
- 8 năm gia nhập WTO: “Nghịch lý” và “lỗi hệ thống” (08.10.2015)
- ASEAN must choose between China, US and a third way (08.10.2015)
- Pentagon Papers (08.10.2015)
- KHỦNG HOẢNG TÀI CHÍNH TOÀN CẦU VÀ NHỮNG TÁC ĐỘNG ĐẾN VIỆT NAM: NHÌN TỪ GÓC ĐỘ NGÂN HÀNG VÀ CHỨNG KHOÁN (08.10.2015)
- “Mua” và “mượn” nhân lực ra sao? (08.10.2015)
- Vietnam defies emerging market slowdown (08.10.2015)
- Vietnams rising repression (08.10.2015)
- Ba trong số những hòn đảo là điểm đến được dân du lịch trẻ nhắc nhiều nhất trong năm nay phải kể đến đảo Lý Sơn (08.10.2015)
- Cận cảnh nơi an nghỉ của đại gia giàu nhất Sài Gòn xưa bên trong nhà thờ Huyện Sĩ (08.10.2015)
- Không để tiền lại cho con (08.10.2015)
- VE VÀ KIẾN (08.10.2015)
- Lá thư viết vào năm 2070... (08.10.2015)
- Người mang bí số TQ2 (08.10.2015)
- Những tấm ảnh để đời chụp những ngày Sài Gòn giải phóng (08.10.2015)
- Làm kinh tế theo lời Phật dạy (08.10.2015)
- Samurai: Một thời kiếm sỹ huyền thoại (08.10.2015)
- Tài tử, giai nhân ngày ấy bây giờ - NSƯT Nguyễn Chánh Tín bán nước đóng chai, mở quán nhậu sống qua ngày (08.10.2015)
- Trịnh Công Sơn tiên cảm về hòa bình, hòa giải và tự do (08.10.2015)
- Về hưu như chết lâm sàng (08.10.2015)
- Vũ trụ sẽ diệt vong như thế nào? (08.10.2015)
- Bài bào chữa Phúc Thẩm (08.10.2015)
- BAI BIEN MINH GỞI VIỆN KS TỐI CAO (08.10.2015)
- Bài biên minh vụ án sản xuất làm giả phân bón gởi bo trưởng bộ congan (08.10.2015)
- Các Quyết định giám đốc thẩm về các tranh chấp liên quan đến thừa kế (08.10.2015)
- CHUYÊN ĐỀ Biện pháp khẩn cấp tạm thời trong tố tụng dân sự (08.10.2015)
- Đề cương bài giảng Luật Tố tụng hình sự (08.10.2015)
- Đơn khiếu này vụ án Tân Uyên (08.10.2015)
- Đơn khiếu nại Phan Thị Trước gửi ỦY BAN NHÂN DÂN THỊ TRẤN TẦM VU (08.10.2015)
- Đơn Kiến nghị Giám đốc Thẩm vụ án dân sự Vicẩm Tú -seoun Tai bai (08.10.2015)
- Đơn khởi kiện Chia di sản long an (08.10.2015)
- Luật đứng về phía con nợ chây ì (08.10.2015)
- Lực lượng thực thi pháp luật chưa nghiêm, tăng mức phạt giải quyết được gì? (08.10.2015)
- 10 loại cây hút khí độc trong nhà cực tốt (08.10.2015)
- Cập nhật phương pháp điều trị suy thận mạn tính (08.10.2015)
- Chữa suy tim (08.10.2015)
- Dược thiện dành cho người bị thiếu máu (08.10.2015)
- Cựu Tổng thống Mỹ Jimmy Carter bị ung thư (08.10.2015)
- Đau nửa đầu bên trái, dấu hiệu bệnh gì? (08.10.2015)
- Điều trị thiếu máu do suy thận mạn thế nào (08.10.2015)
- Dù đã bước vào tuổi 100 (08.10.2015)
- Ghép tế bào gốc cuộc cách mạng” trong điều trị bệnh lý về máu (08.10.2015)
- Già Sao Cho Sướng! (08.10.2015)
- Những điều cần biết về bệnh suy tủy (08.10.2015)
- Khi bạn qua tuổi 65, hãy hưởng thụ những gì mình yêu thích… (08.10.2015)
- Nhiều người Mỹ không muốn sống hơn 100 tuổi (08.10.2015)
- Thang Thuốc Trường Thọ từ dân gian Trung Hoa (08.10.2015)
- THIẾU MÁU (08.10.2015)
- Thủ tướng Singapore bàn về Biển Đông tại trường đảng của Trung Quốc (08.10.2015)
- Việt Nam cần học gì từ quân sự Nhật? (08.10.2015)
- Will China crash? (08.10.2015)
- The Truth About US Freedom of Navigation Patrols in the South China Sea (08.10.2015)
- Tàu sân bay Mỹ sắp hết thời ? (08.10.2015)
- Nhật sẽ cấp thêm tàu cho Việt Nam (08.10.2015)
- Ngày này tháng 1/ 1974: Kissinger và vụ Hoàng Sa! (08.10.2015)
- China's Meltdown Goes Deeper Than the Stock Market (08.10.2015)
- China's FakeIslands in the South China Sea: What Should America Do? (08.10.2015)
- BÀI VIẾT PHÂN TÍCH Chiến tranh với Trung Quốc (08.10.2015)
- ASEAN must choose between China, US and a third way (08.10.2015)
- 10 lý do khiến Trung Quốc gặp khó khăn trong chiến tranh hiện đại (08.10.2015)
- Thủ Thiêm gần hết đất để phát triển khu dân cư (08.10.2015)
- Sức sống của cát (08.10.2015)
- Trung Quốc: “Bệnh đô thị” ngày càng lây lan (08.10.2015)
- Dự Đoán Địa ốc 2007-2015 (08.10.2015)
- Doanh nghiệp bất động sản Tp Hồ Chí Minh (08.10.2015)
- Chuyên đề tiền vào bất động sản 2015 (08.10.2015)
- Chuyên đề Bất động sản 2015 bắt đầu cho đợt sóng lớn năm năm bền vững ?!!! (08.10.2015)
- ‘Của để đời’ của những đại gia lạ trong giới BĐS (08.10.2015)
- Già ơi, Chào Mi! (04.09.2015)
- Làm thế nào để giảm nguy cơ tai biến mạch máu não ở phụ nữ (04.09.2015)
- Những cái cũ & xưa nhất của Saigon (27.08.2015)
- Nguyên Nhân Thành Công Của Những Người gốc Do Thái ??? (27.08.2015)
- HÌNH ẢNH SAIGON qua máy ảnh người nước ngoài (27.08.2015)
- Một khúc ca xuân! (Tố Hữu) (27.08.2015)
- 10 câu hỏi dành cho nhà vật lý lỗi lạc nhất hiện nay, Stephen Hawking (27.08.2015)
- Bí ẩn tuyệt tự của 3 đời vua cuối cùng nhà Thanh (27.08.2015)
- TRỜI PHẬT DẠY VỀ THỜI GIAN - NGHIỆP BÁO (27.08.2015)
- ĐẮNG VÀ NGỌT (27.08.2015)
- Thư giãn với những hình ảnh đẹp của thiên nhiên (27.08.2015)
- Bài thơ Vấn thoại của Hồ Chí Minh và vụ án oan của ông Nguyễn Thanh Chấn – trandinhsu P2 (27.08.2015)
- Vui trồng hoa thay vì buồn nhổ cỏ (27.08.2015)
- Khám phá Ðèo Ngang (27.08.2015)
- Bài thơ : “Vội” (27.08.2015)
- A Tribute to the Dog - bài diễn văn bất hủ ngợi ca con chó (27.08.2015)
- Cõi già trên Đất Lạ (27.08.2015)
- Thiền và kinh tế học "Thủy tự mang mang hoa tự hồng (27.08.2015)
- Cha con cạn tình (27.08.2015)
- Cha, con và miếng đất (27.08.2015)
- trước cau sau chuối (27.08.2015)
- Điên Vì Đàn Bà (27.08.2015)
- Anh xin thề (27.08.2015)
- Ai ? (27.08.2015)
- Phút thật lòng (27.08.2015)
- Vợ nghĩ gì về chồng (27.08.2015)
- Thời @ (27.08.2015)
- Ba con quỷ (27.08.2015)
- Đỉnh cao đối đáp (27.08.2015)
- Trung Quốc và thế giới (27.08.2015)
- Trung Quốc trắng trợn lộ kế hoạch đánh chiếm đảo thuộc Trường Sa năm 2014 (27.08.2015)
- Thẩm định về ” Thế Kỷ Trung Quốc ?” (27.08.2015)
- Mỹ đang giữ liên lạc chặt chẽ với Việt Nam về vụ giàn khoan Trung Quốc (27.08.2015)
- Mỹ: Trung Quốc phải làm rõ tuyên bố chủ quyền Biển Đông theo UNCLOS (27.08.2015)
- Liệu có xảy ra chiến tranh tại Biển Đông? (27.08.2015)
- Kiện TQ, cơ hội thắng của Việt Nam đến đâu? (27.08.2015)
- Kiềm chế, đối thoại và tuân thủ luật pháp quốc tế (27.08.2015)
- Giàn khoan Hải Dương 981 vướng núi đá ngầm Việt Nam (27.08.2015)
- Giàn khoan Hải Dương 981 “vào giai đoạn hai” (27.08.2015)
- Giải mã tín hiệu chiến tranh của Trung Quốc - Kỳ 3 (27.08.2015)
- ĐÃ ĐẾN LÚC VIỆT NAM PHẢI QUYẾT ĐỊNH! (27.08.2015)
- Biển Đông: Thế trận mới đang hình thành (27.08.2015)
- Đương đầu với thách thức từ Trung Quốc (27.08.2015)
- Đội Hoàng Sa và bí mật quân lương (27.08.2015)
- Bộ trưởng Quốc phòng Việt Nam, Đại tướng Phùng Quang Thanh, vừa có chuyến thăm chính thức Hoa Kỳ. (27.08.2015)
- Mạ Lê Thị A (27.08.2015)
- 49 điều cha dạy con 2014 (27.08.2015)
- Bà mẹ Việt Nam (27.08.2015)
- Nhật ký ông Nội phần 3 (27.08.2015)
- Hồi ký Ông nội -phần 2 (27.08.2015)
- Hồi ký Ông nội -phần 1 (27.08.2015)
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự tập 10 (27.08.2015)
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự tập 9 (27.08.2015)
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự tập 8 (27.08.2015)
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự tập 6 (27.08.2015)
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự tập 5 (27.08.2015)
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự tập 4 (27.08.2015)
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự tập 3 (27.08.2015)
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự tập 2 (27.08.2015)
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự tập 1 (27.08.2015)
- Bình luận khoa học hình sự tập 1 (26.08.2015)
- Luật dân sự 2005 (26.08.2015)
- Đơn khởi kiện đòi nợ vay (26.08.2015)
- ĐƠN YÊU CẦU GIẢI QUYẾT KHIẾU NẠI (26.08.2015)
- Bàn về xác minh điều kiện thi hành án (26.08.2015)
- Nghị Định 84-2007-CP giấy quyền SD đất (26.08.2015)
- Nghị Định 84-2007-CP giấy quyền SD đất (26.08.2015)
- GIẢI QUYẾT CÁC TRANH CHẤP LIÊN QUAN ĐẾN QUYỀN SỬ DỤNG ĐẤT TẠI TOÀ ÁN NHÂN DÂN (26.08.2015)
- THÔNG TƯ 70 BỘ CÔNG AN QUY ĐỊNH CHI TIẾT THI HÀNH CÁC QUY ĐỊNH CỦA BỘ LUẬT TỐ TỤNG HÌNH SỰ LIÊN QUAN ĐẾN VIỆC BẢO ĐẢM QUYỀN BÀO CHỮA TRONG GIAI ĐOẠN ĐIỀU TRA VỤ ÁN HÌNH SỰ (26.08.2015)
- Nghị định xử phạt hành chính trong lĩnh vực tư pháp có hiệu lực từ ngày 18-9: (26.08.2015)
- Nghị quyết của Hội đồng Thẩm phán Tòa án nhân dân tối cao số 02/2004/QĐ-HĐTP ngày 10-8-2004 hướng dẫn áp dụng pháp luật trong việc giải quyết các vụ án dân sự, hôn nhân và gia đình (26.08.2015)
- Luật Thương mại 2005 (26.08.2015)
- Luật Doanh Nghiệp năm 2005 (26.08.2015)
- Nghị Định 14/2007/NĐ-CP (26.08.2015)
- Luật quy định về hoạt động chào bán chứng khoán ra công chúng, niêm yết, giao dịch, kinh doanh, đầu tư chứng khoán, dịch vụ về chứng khoán và thị trường chứng khoán. (26.08.2015)
- luật dân sự (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH 121/2007/NĐ-CP (26.08.2015)
- THÔNG TƯ 59/2007/TT-BTC (26.08.2015)
- THÔNG TƯ 61/2007/TT-BTC (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH 35/2006/NĐ-CP (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH 59/2006/NĐ-CP (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH 158/2006/NĐ-CP (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH 52/2006/NĐ-CP (26.08.2015)
- THÔNG TƯ 09/2007/TT-BTM (26.08.2015)
- LUẬT NGƯỜI LAO ĐỘNG VIỆT NAM ĐI LÀM VIỆC Ở NƯỚC NGOÀI THEO HỢP ĐỒNG (26.08.2015)
- LUẬT SỬA ĐỔI, BỔ SUNG MỘT SỐ ĐIỀU CỦA BỘ LUẬT LAO ĐỘNG (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH 133/2007/NĐ-CP (26.08.2015)
- THÔNG TƯ 38/2007/TT-BTCTHÔNG TƯ 17/2007/TT-BTC (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH 140/2007/NĐ-CPNGHỊ ĐỊNH 139/2007/NĐ-CP (26.08.2015)
- Quy trình cấp giấy phép xây dựng (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ QUYẾT 48/2007CP-NĐ (26.08.2015)
- BỘ LUẬT DÂN SỰ (26.08.2015)
- Quy định chi tiết thi hành các quy định của Bộ luật dân sự (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH 126/2007/NĐ-CP (26.08.2015)
- THÔNG TƯ 17/2007/TT-BTC (26.08.2015)
- THÔNG TƯ 38/2007/TT-BTC (26.08.2015)
- PHÁP LỆNH THỪA KẾ (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH 139/2007/NĐ-CP (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH 140/2007/NĐ-CP (26.08.2015)
- Quy trình cấp giấy phép xây dựng (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ QUYẾT 48/2007CP-NĐ (26.08.2015)
- BỘ LUẬT DÂN SỰ (26.08.2015)
- Quy định chi tiết thi hành các quy định của Bộ luật dân sự (26.08.2015)
- Quy định chi tiết thi hành Luật Thuế thu nhập doanh nghiệp (26.08.2015)
- Quy định chi tiết thi hành một số điều của Luật Quản lý thuế (26.08.2015)
- LUẬT KINH DOANH BẤT ĐỘNG SẢN (26.08.2015)
- THONG TU 59 NAM 2004 (26.08.2015)
- NGHI DINH 100 NAM 2006 (26.08.2015)
- Luật Sở Hữu Trí Tuệ (26.08.2015)
- NGHI DINH 70 NÁM997 (26.08.2015)
- NGHI DINH 142 NAM 2005 (26.08.2015)
- QUYẾT ĐỊNH 54 NĂM 2007 (26.08.2015)
- NGHI DINH 123 NAM 2007 (26.08.2015)
- NGHI DINH 90 NAM 2006 (26.08.2015)
- NGHI DINH 84 NAM 2007 (26.08.2015)
- luật đất đai (26.08.2015)
- LUẬT CƯ TRÚ (26.08.2015)
- LUẬT QUẢN LÝ THUẾ (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH CỦA CHÍNH PHỦ SỐ 103/2006/NĐ-CP NGÀY 22 THÁNG 9 NĂM 2006 (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH CỦA CHÍNH PHỦ SỐ 36/2007/NĐ-CP NGÀY 08 THÁNG 3 NĂM 2007 VỀ XỬ PHẠT VI PHẠM HÀNH CHÍNH TRONG LĨNH VỰC CHỨNG KHOÁN (26.08.2015)
- NGHỊ ĐỊNH 163/2006/NĐ-CP ngày 29 tháng 12 năm 2006 quy dịnh về đăng ký giao dịch bảo đảm. (26.08.2015)
- những câu hỏi thường gặp (26.08.2015)
- Cấp thẻ APEC cho doanh nhân VN (26.08.2015)
- CỘNG HOÀ XÃ HỘI CHỦ NGHĨA VIỆT NAM Độc lập - Tự do - Hạnh phúc ------------------------- GIẤY ĐỀ NGHỊ ĐĂNG KÝ KINH DOANH CÔNG TY HỢP DANH Kính gửi: Phòng đăng ký kinh doanh................................................. (26.08.2015)
- GIẤY ĐỀ NGHỊ ĐĂNG KÝ KINH DOANH CÔNG TY HỢP DANH (26.08.2015)
- DANH SÁCH CÁC THÀNH VIÊN CÔNG TY HỢP DANH (26.08.2015)
- HƯỚNG DẪN XÂY DỰNG ĐIỀU LỆ CÔNG TY HỢP DANH (26.08.2015)
- DANH SÁCH CÁC THÀNH VIÊN CÔNG TY TRÁCH NHIỆM HỮU HẠN CÓ (26.08.2015)
- ĐIỀU LỆ CÔNG TY TNHH CÓ HAI THÀNH VIÊN TRỞ LÊN (26.08.2015)
- HƯỚNG DẪN SOẠN THẢO DANH SÁCH CỔ ĐÔNG SÁNG LẬP CÔNG TY CỔ PHẦN (26.08.2015)
- GIẤY ĐỀ NGHỊ ĐĂNG KÝ KINH DOANH (26.08.2015)
- HƯỚNG DẪN ĐIỀU LỆ CÔNG TY CỔ PHẦN THEO QUY ĐỊNH LUẬT DOANH NGHIỆP 2005 (26.08.2015)
- 10 cổ phiếu giá bèo khởi sắc nhất sàn (26.08.2015)
- Qũy PXP Vietnam: "Chúng ta đang ở giai đoạn đầu của thị trường bò tót" (26.08.2015)
- 5 sai lầm của các nhà đầu tư chứng khoán Việt Nam (26.08.2015)
- 10 BÍ QUYẾT LÀM GIÀU CỦA WARREN BUFFETTY PHÚ GIÀU NHẤT THẾ GIỚI (26.08.2015)
- “Vô tư” hủy lệnh giữa phiên (26.08.2015)
- Công ty chứng khoán chưa chuyên nghiệp! (26.08.2015)
- Nhà đầu tư cần biết (26.08.2015)
- có sốt chứng khoán cuối năm (26.08.2015)
- Phát hành thêm = mua cổ phiếu giá rẻ? (26.08.2015)
- 100 người giàu nhất Việt Nam trên sàn chứng khoán (26.08.2015)
- Dự báo TTCK sẽ tăng mạnh trong 4 năm tới (26.08.2015)
- Sàn chứng khoán TP HCM lại tê liệt (26.08.2015)
- Thấy gì qua những doanh nghiệp thuỷ sản niêm yết? (26.08.2015)
- Ra mắt Công ty Chứng khoán Âu Lạc (26.08.2015)
- Thủ tục lưu ký quá chậm trễ vì sao? (26.08.2015)
- Thị trường chứng khoán: Những dự báo và bài học từ Thái Lan (26.08.2015)
- Sự phát triển thị trường chứng khoán và những ảnh hưởng của nó đến hoạt động ngân hàng trong năm 2006 (26.08.2015)
- Tọa đàm khoa học nghiệp vụ "Kinh nghiệm trong công tác kiểm sát giải quyết án dân sự về tranh chấp đất đai, nhà ở" (25.08.2015)
- Khổ vì trót mua nhà đất là tài sản thi hành án (25.08.2015)
- CHƯƠNG 3 CHỐN LAO TÙ LÀ NƠI TA RÈN TÂM TRÍ 20tr (25.08.2015)
- Án thi hành xong bị lật lại : Rối! (25.08.2015)
- Những người góp phần tạo nên tình thế (25.08.2015)
- tiểu thuyết Điệp Báo A10- bản gốc (25.08.2015)
- ÔNG 10 HƯƠNG: TRÁCH NHIỆM - GÁNH VÁC – NHÂN VĂN (25.08.2015)
- Cụm điệp báo A10 và họa sĩ Ớt (25.08.2015)
- Gặp 1 trong 5 người tố cáo chuồng cọp (25.08.2015)
- Thời hiệu khởi kiện về thừa kế: Mốc để tính là khi nộp đơn kiện (25.08.2015)
- 10 loại giấy tờ để xác định thời điểm bắt đầu sử dụng đất (25.08.2015)
- Hướng dẫn giải quyết tranh chấp đất đai (25.08.2015)
- Lập thủ tục mua bán hoặc thừa kế nhà và xin chuyển quyền sử dụng đất (25.08.2015)
- Việt kiều vẫn có quyền hưởng thừa kế (25.08.2015)
- Tranh chấp nhà ở mà một bên định cư ở nước ngoài (25.08.2015)
- Các dạng tranh chấp đất đai phổ biến hiện nay (25.08.2015)
- Tháo gỡ ách tắc trong giải quyết tranh chấp đất đai (25.08.2015)
- Cơ hội nào cho Trần Nhựt Thành? (25.08.2015)
- Những dấu chân rời sau Núi Mộng (25.08.2015)
- Đằng sau một bản án treo (25.08.2015)
- Úp, ngửa cũng là bàn tay (25.08.2015)
- Chuyện buồn ngoài sân tòa (25.08.2015)
- Mẹ con ra tòa (25.08.2015)
- Áo trắng học trò trước vành móng ngựa (25.08.2015)
- Không có hộ khẩu ở Hà Nội có mua đất được không? (25.08.2015)
- Mang hộ chiếu VN còn hiệu lực thì không cần thị thực khi về nước (25.08.2015)
- Thủ tục cải chính họ tên (25.08.2015)
- Nhập hộ khẩu theo chồng hoặc vợ (25.08.2015)
- Giấy khai sinh của con tôi để trống phần tên cha (25.08.2015)
- Xin phiếu lý lịch tư pháp ở đâu? (25.08.2015)
- Chúng tôi không muốn có mặt tại tòa khi ly hôn (25.08.2015)
- Muốn khởi kiện dân sự làm thế nào? (25.08.2015)
- Tranh chấp nhà ở trước 1/7/1991 có yếu tố nước ngoài (25.08.2015)
- Nhập hộ khẩu theo chồng hoặc vợ (25.08.2015)
- Ai là người giàu trên con đường công nghiệp hóa? (25.08.2015)
- Lính bộ binh vào Dinh Độc Lập (25.08.2015)
- XỨ MỸ PHIỀN TOÁI (25.08.2015)
- Một Nước Nhật Quá Xa Xôi (25.08.2015)
- Viễn tưởng (25.08.2015)
- Lý Quang Diệu đánh giá lãnh đạo Trung Quốc (25.08.2015)
- Gót chân Ashin của Trung Quốc (25.08.2015)
- TỘI ÁC CỦA TƯ BẢN (25.08.2015)
- Thời kỳ thoái đã bắt đầu từ lâu - Dự báo 60 năm phần 2 (25.08.2015)
- Dự báo 60 năm đầu thế kỷ 21 và hướng đến thế kỷ 22 (25.08.2015)
- Bài diễn văn của Mục Sư Martin Luther King, Jr (25.08.2015)
- Tham luận về những vấn đề cần rút kinh nghiệm trong công tác xét xử sơ thẩm và phúc thẩm các (25.08.2015)
- Chuyên đề khó khăn trong thi hành án (25.08.2015)
- Nước Mỹ nợ tới hơn 100 nghìn tỷ USD!a ha ! chỉ cần lấy 1/3 dành cho Quân Đội ,1/3 nắm vàng là xong (25.08.2015)
- Giá phải trả của 12 năm kinh tế phi thị trường (25.08.2015)
- Cải cách luật pháp đáp ứng đòi hỏi WTO (25.08.2015)
- Việt Nam gia nhập WTO, những cơ hội và thách thức đối với lĩnh vực văn hóa (25.08.2015)
- Những bất lợi khi bị coi là nền kinh tế phi thị trường (25.08.2015)
- MƯỜI NGUYÊN TẮC THỌ THÊM NHIỀU TUỔI (24.08.2015)
- Một phút suy tư về chữ TÂM ... (24.08.2015)
- gởi các Bạn trên 60 tuổi và còn khỏe mạnh (24.08.2015)
- TUỔI GIÀ LÀ THỜI SUNG SƯỚNG NHẤT (24.08.2015)
- TÔI ÐÃ ÐỨNG TRÊN NGƯỠNG CỬA CỦA CÁI CHẾT (24.08.2015)
- Đăng Sâm chữa bệnh cao huyết áp (24.08.2015)
- CÂY KẾ SỮA (24.08.2015)
- Con người có thể sống đến 500 tuổi nhờ khoa học gen (24.08.2015)
- Phát Biểu của Ðức Ðạt Lai Lạt Ma Thứ 14 TENZIN GYATSO Về Vấn Ðề Tái Sanh của Ngài (24.08.2015)
- Bài thuốc về các loại đậu (24.08.2015)
- bí thuật hồi xuân Tây Tạng 2 (24.08.2015)
- bí mật hồi xuân Tây Tạng 3 (24.08.2015)
- bí thuật hồi xuân Tây Tạng 1 (24.08.2015)
- Bí quyết An Khang: Ăn, Ngủ, Thở (24.08.2015)


















































 Yahoo:
Yahoo: 